 |
|
|
1582 - Rourteau, great French chef, opened
L'Hostellerie de La Tour d'Argent (La Tour d'Argent), elegant
inn, in Paris (named for silvery reflection of its original
16th-century walls in river Seine); catered to aristocrats;
March 4, 1582 -
Henri, King of Poland and France, introduced the 'fork';
1600 - Rourteau as
proprietor; 1720 -
introduced theater suppers; 1890
- acquired by Frederic Delair; introduced signature dish,
specialty of the restaurant: 'Caneton
Tour D'Argent', pressed duck ("Canard au Sang"); numbered each
duck (number 328 served to King Edward VII in 1890, number
14,312 served to King Alfonso XIII in 1914, number 112,151
served to Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1929, number 938,451 served
to President Mikhail Gorbachev in 2001); 1912 - acquired by
Andre Terrail; 1918
- reopened after end of WW I;
1925 - Terrail built Hotel George V;
May 6, 1929 -
served 100,00th 'Caneton Tour D'Argent';
1947 - Claude Terrail (son) took over;
1984 - opened La
Tour d'Argent Tokyo; 1990
- 100th anniversary of 'numbered duck';
2003 - served 1
millionth duck; June 1, 2006
- Andre Terrail (grandson) took over.
 Frederic Delair
- La Tour D'Argent
(http://www.linternaute.com/sortir/sorties/resto/dossier/06/la-tour-dargent/images/02ter.jpg)
Frederic Delair
- La Tour D'Argent
(http://www.linternaute.com/sortir/sorties/resto/dossier/06/la-tour-dargent/images/02ter.jpg)
December
13, 1827 - Giovanni Del-Monico,
Swiss wine merchant,
Pietro (older brother) opened Delmonico & Brother, café, pastry shop
at 23 William St. in lower
Manhattan; March, 1830
- opened restaurant at 25 William Street (first restaurant or
public dining room opened in United States);
December 16, 1835 -
destroyed by fire; August 1837 - Delmonico's restaurant
re-opened at corner of Beaver, William and South William.
1840
- Antoine Alciatore (27) opened pension, boarding house,
restaurant on St. Louis Street in New Orleans, LA; 1868
- moved to spot on St. Louis Street where restaurant stands
today; 1887 - Jules (son) took over; invented
Oysters Rockefeller, named for richness of sauce;
1932 - Roy Louis (son) took over, headed restaurant for
almost 40 years until his death in 1972; Marie Louise (Roy's
daughter) married William Guste; Alciatore-Guste family members
have guided restaurant to present day.
1849
- Nikola Budrovich, Antonio Gasparich, Frank Kosta (Croatian
immigrants) opened New World Coffee Saloon
on Commercial Street in
San Francisco, CA; 1876 - John Tadich (Croatian
immigrant) began working at Saloon; 1882 - owners
Samuel Becir, Eugene Masounette changed name to "Cold Day
Restaurant" (Alexander Badlam Jr. defeated in 1882 Assessors
Election, "It's a cold day when I get left" slogan); 1883
- Becir interest acquired by Gaspar Pavica; 1887 -
Masounette's interest acquired by Tadich; 1888 -
bought out Pavica, assumed full ownership of restaurant;
August 26, 1912 - renamed Tadich's Grill, located at 525
Clay St.; 1928 - acquired by three Buich brothers
(employees since 1913); 1961 - full ownership
acquired by Louie Buich (last brother employed under Tadich, in
1922); 1967 - redeveloped, moved to current
location at 240 California Street; 1993 - interest
passed to Steve Buich (third generation); oldest restaurant in
State of California.
February 1855
- El Nivel ( the
"level", previously building where water level in Mexico City
was measured) in Mexico City received first cantina license
after the U.S.-Mexican war (holds liquor license #1);
prior to 1968 - acquired by Jesus Aguirre; around 30
presidents from Sebastian Lerdo de Tejada in 1872 to Ernesto
Zedillo (1994-2000) had visited for a drink while in office;
January 2, 2008 - closed, lost long legal battle
against owners of building, National Autonomous University of
Mexico.
1863 - Senator John
Buckley and C. C. Butler built Cliff House in San Francisco,
CA; 1868 -
remodeled by Captain Junius Foster;
1883 - acquired Adolph Sutro;
1885 - leased to J.
M. Wilkins; 1887
- severely damaged when schooner Parallel, abandoned and loaded
with dynamite, ran aground on rocks below;
February 1896 - second Cliff House
opened (furnished in grandiose style at cost of $75,000;
fashioned after French chateau, eight stories, four spires,
observation tower 200 feet above sea level); June
1907 - leased to John Tait (Tait’s at the
Beach), and seven partners; September
7, 1907 - burned to ground (after extensive
remodeling, just prior to reopening); July
1, 1909 - third version of the Cliff House
opened; rebuilt by Dr. Emma Merritt, daughter of Adolph Sutro,
John Tait, group of investors, on behalf of Sutro estate, at
cost of $75,000 (neoclassical in design, built with steel
reinforcing bar, poured concrete); 1918
- shut down due to military orders signed by President of the
United States; December 1920
- leased from Charles Sutro by Shorty Roberts
(Roberts-at-the-Beach restaurant);
1925 - closed (due to Prohibition); December
1937 - acquired by George and Leo Whitney,
owners of Playland; August 1938
- reopened after extensive remodeling;
1977 - acquired by Golden Gate National
Recreation Area.
 Adolph Sutro
- Cliff House
(http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/
thumb/f/fe/Adolph_Sutro_by_Brady.jpg/225px-Adolph_Sutro_by_Brady.jpg)
Adolph Sutro
- Cliff House
(http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/
thumb/f/fe/Adolph_Sutro_by_Brady.jpg/225px-Adolph_Sutro_by_Brady.jpg)
1864 - Frenchman
George Voges opened Jack's in San Francisco; acquired by Jacques
Monique; acquired by Edward Blanque; 1907 -
acquired by Michel Redinger, became part owner after putting in
money to rebuild after the 1906 earthquake; Paul Redinger
(brother) bought out Edward Blanque's share; eventually Jack
Redinger (son) became owner; 1930 - made famous in Maltese
Falcon, written by Dashiell Hammett; December 1996
- acquired by John Konstin (including the building), owner of
John's Grill, for $132 million.
1872
- Walter Scott's business selling sandwiches became so
lucrative, quit his printing work (part-time pressman, type
compositor in Providence, RI), began to sell food at night from
horse-drawn covered express wagon parked outside Providence
Journal newspaper office; inspired birth of "the diner".
1875
- Luis Ober filed an application to remodel numbers 3 and 4
Winter Place (Boston, MA) into café and dwelling; Eben Jordan,
co-founder of Jordan Marsh Company, supposedly advanced funds
needed to purchase, remodel the buildings; restaurant opened as
Ober’s Restaurant Parisien; 1892 - Frank Locke’s
Wine Rooms opened for business at Nos. 1 and 2 Winter Place as
competition for Ober; 1894 - Ober sold business to
Wood and Pollard, firm of wholesale liquor dealers; May 1894
- acquired Wine Rooms from Locke's estate (died at 46);
buildings combined by breaking through wall separating Locke’s
from Ober’s; renamed Winter Place Tavern; 1898 -
acquired by John Merrow, renamed The Winter Place Hotel; went
bankrupt; April 27, 1901 - Emil Camus formed The
Locke-Ober Company; secured services of Mr. J.B. Bailhe, Ober's
famous French chef for many years; 1981 -
restaurant finally recovered original Locke’s location in full;
2001 - acquired by Winter Place LLC; operated in
same configuration as in 1910 under Camus; second oldest
restaurant in Boston.
1877 - Café
Brasilero opened in Montevideo, Uraguay; longest operating cafe;
essential cultural legacy of Montevideo’s Old City.
1883 - Johnny
Heinold opened J.M. Heinold's Saloon at foot of Webster Street
in Oakland, CA; paid $100 for former bunk house for men working
nearby oyster beds; built from timbers of an old whaling ship;1920's
- ferry between Alameda (dry town) and Oakland stopped next to
Heinold's (commuter's First and Last Chance for refreshment);
name changed to Heinold's First and Last Chance; referenced
seventeen times in Jack London's novel John Barleycorn.
September 4, 1885 - Exchange Buffet opened at 7
New Street, New York City; served men only; first self-serve
restaurant in U.S.
May 1, 1886 -
Angelo Del Monte, 'Papa' Marianetti opened Ristorante Fior
d'Italia, America's oldest Italian restaurant, in heart of San
Francisco's North Beach to serve clients of nearby bordello;
1893 - original gold rush era building burned;
restaurant grew to size that could seat 750, serve 1500 meals a
day; Frank and George Marianetti (sons) took over; sold to group
(Sergio and Larry Nibbi, Charles Ramorino, Achille Pantaleoni,
Armanino); 1990 - acquired by Bob and Jinx Larive,
Hamish and Rosi Fordwood; February 15, 2005 - fire
destroyed restaurant; 2005 - moved to new location
in San Remo Hotel on Mason Street; Bob and Jinx Larive bought
out other partners.
1887
- Peter Luger, German immigrant, opened steak house in Brooklyn;
1941 - Luger died, succeeded by son; 1950
- acquired at auction (for price of the real estate) by Sol
Forman, owner of metalware business across street.
September 1, 1887
- Saugus Train Station dedicated; named for birthplace of Henry
M. Newhall in Massachusetts (Narragansett Indian term means
sandy spit of land); Joseph Herbert Tolfree started Saugus
Eating House in north end of depot; April 25, 1891
- President Benjamin Harrison had a meal while on whistle
stop re-election campaign; January 18, 1899 -
acquired by Richard R. Wood, Southern Pacific Railroad employee,
and Martin Wood (brother), name changed to Saugus Café;
May 1903 - President Theodore Roosevelt had dinner;
1926 - Helen Wood married Bryon Cone, took over;
1936 - Fielding S. Wood took over management;
1974 - Fred Kane took over; 1979 -
acquired by Steve Hwang; November 1983 - closed due to financial
difficulties; rescued by Fred Kane; February 1, 1994
- acquired by Karen and David Nardiello.
December 22, 1888 - Joseph V.
Horn, Frank Hardart founded Horn & Hardart, 15-stool lunchroom,
in Philadelphia, PA; 1898 - incorporated as
Horn & Hardart Baking Co.; 1902 - opened first
Automat ('waiterless') restaurant; grew to 84 stores in
New York, Philadelphia; 1971 - filed for
bankruptcy; 1972 - acquired Hanover House
Industries, mail-order company in Hanover, PA; 1977
- acquired by Barry Florescue, Burger King franchisee from
Florida; October 1991 - acquired by North American
Resources, international investment group; 1993 -
name changed to Hanover Direct (15 retail catalogs).
1889 - William and Samuel Chillds opened Childs
Restaurant on Cortland Street in Manhattan (had $1600,
second-hand furniture); 1898
- opened self-service cafeteria at 130 Broadway; introduced
tray, tray line to customers (carry their meals to tables);
1899 - 10
restaurants; 1902 -
incorporated; 1925
- 107 restaurants in 33 cities;
1939 - awarded food service contract for New
York World's Fair; 1950s
- acquired by Lucky Stores; 1961
- acquired by Reise Brothers.
1889
- Former Tempe, AZ residence of Charles Trumbull Hayden (settled
in Arizona in 1871 to establish flourmill, ferry service for
crossing Salt River) run as restaurant, as convenience to those
who had traveled great distance to use flourmill or ferry
service; 1924 -
major renovation by Hayden sisters;
1930 - financial difficulties forced
sale of property; 1943-1947
- operated by Lucille and Eugene Payne;
1954 - acquired by Leonard F. Monti, Sr.
(had operated 13-stool diner in Chandler, AZ since 1946);
April 1956 - opened
for business; March 28, 1972
- Monti's La Casa Vieja Restaurant, Inc. registered "La Casa
Vieja" ("The Old House in Spanish) trademark first used February
22, 1956 (restaurant services);
2010 - serves approximately 500,000 customers
annually.
1890
- Johan Spenger, hook and line fisherman on Lake Merritt,
California, opened clam stand at 1919 Fourth St., Berkeley, CA;
sold day's catch from one-room lean-to gabled house in mud flats
in Ocean View community; 1933
- Frank Spenger Sr. (son), also fisherman, added restaurant and
tavern (turned little fish shack into bar "with four stools
nailed to the floor"); named Spenger’s Fresh Fish Grotto;
1940-1998 - managed
by Frank “Buddy” Spenger Jr. (grandson);
1950s - claimed to serve roughly 3,500
pounds of fish daily, more than any restaurant west of
Mississippi; 1998 -
closed temporarily (competition from 'California cuisine');
acquired by McCormick & Schmick Seafood Restaurants (Portland,
OR).
1894 - Frank
Duarte brought barrel of whiskey from Santa Cruz to
establishment in Pescadero, CA; price was ten cents for one
whiskey, two bits for three; business thrived until prohibition;
1934 - second generation reopened bar; 1950s
- third generation joined; 1961 - widow took over;
mid-1980s - fourth generation arrived; May
2003 - James Beard Foundation awarded Duarte's honorary
award as American Classic (one of five restaurants in United
States honored); 2007 - serve average of 13,000
people a month; have grown from two employees in the fifties to
sixty-five; extensive menu focused on artichoke dishes, fresh
fish, wine list of over two hundred different labels.
1893 - Henry
Schroeder opened Schroeder's Restaurant on the south side of
Market between First and Second Streets in San Francisco;
1921 - his widow took over; January 10, 1922
- acquired, sight unseen, by Max Kniesche with gold pieces;
1935 - began serving dinner, opened to ladies after
1:30 p.m.; 1959 - moved to present locale at 240
Front Street; October 7, 1970 - opened to ladies
for lunch; April 1997 - acquired by Jana and
Stefan Filipclk, immigrants from Reichenberg, Czech Republic;
oldest, largest German restaurant on West Coast.
1898 - Herman
Joseph Berghoff opened Berghoff Cafe, at corner of State and
Adams Streets (Chicago, IL), to showcase celebrated
Dortmunder-style beer; sold beer for nickel, sandwiches for
free; 1933 -
Prohibition repealed, city issued liquor license No. 1 to
Berghoff (done so each year since); 1969 - separate men's only
bar ended; seven members of National Organization for Women sat
at bar, demanded service; got it;
December 28, 2005 - third-generation announced
Berghoff would close on February 28, 2006.
June 19, 1902 -
Horn & Hardart Automat Restaurant opened at 818 Chestnut Street
in Philadelphia; first restaurant with vending machine service;
cavernous, waiterless establishment - combination of fast-food,
vending, cafeteria; 1912
- expanded to Manhattan; first major fast-food chain with
uniform recipes, centralized commissary system of supplying
their restaurants; customers put nickels into slots, turned
knob, food revolved into place in compartment next to slot for
customer to receive through small glass door.
1904 - Robert
Cascarelli opened fruit, vegetable, candy shop at 109 N.
Superior St., Albion, MI; January
7, 1908 - moved to 116 S. Superior St.;
1929 - Louis
Cascarelli (son) took over business;
1930s - became tavern;
1970 - Jim
Cascarelli (grandson) took over family business;
January 7, 2009 -
anniversary celebration (by invitation only - 300 family,
friends, vendors); Bell's Brewery of Kalamazoo crafted
Cascarelli's 100th Anniversary Ale just occasion.
1905 -
City of
New York issued mercantile license to Genaro Lombardi, baker and
pizziolo from Naples, Italy; opened Lombardi's, nation's first
licensed pizzeria, on Spring St., in lower Manhattan (opened as
grocery store in 1897); 1984
- closed; 1994 -
reopened by friend of grandson.
1907 - Harley
Hudson opened the Missouri Kitchen, a "quick-eats" lunch stand
in tent on Sherman Avenue in Coeur d'Alene, Idaho's main street;
five generations of Hudsons have continuously operated Hudson's
Hamburgers Restaurant; January 24, 2007 - Idaho
state legislature issued Proclamation "to recognize and honor an
Idaho business and the Hudson family for 100 years of business
in Coeur d'Alene, Idaho".
 Harley Hudson
- Hudson's - Coeur d'Alene
(http://www.spokesmanreview.com/blogs/video/thumbs/031007_hudsons.jpg)
Harley Hudson
- Hudson's - Coeur d'Alene
(http://www.spokesmanreview.com/blogs/video/thumbs/031007_hudsons.jpg)
1908
- Philippe Mathieu established Philippe The Original in Southern
California; 1918 -
claimed distinction of having created "French Dipped Sandwich";
1927 - acquired by Harry, Dave, Frank Martin for about $5,000;
1977 - price of cup of coffee increased 100%, to a dime.
1911 - Harry Luby founded New England Dairy Lunch cafeterias in
Springfield, MO; 1920 - opened restaurant in Waco, TX;
1934 -
Robert M. Luby (son) established his first Luby's Cafeteria at
Dallas; 1959 - company incorporated as Cafeterias, Incorporated,
operated nine cafeterias in Texas; 1981 - name changed to Luby's
Cafeterias, Incorporated; 1982 -operated sixty-three cafeterias,
mostly in Texas; 1990 - employed 9,500 workers at 175 locations
in ten states; 1991 - George Hennard killed twenty-three people,
injured numerous others at Luby's Cafeteria in Killeen, TX;
1987-1996 - over-expansion more than doubled company's size, 226
restaurants in 11 states; pushed into bankruptcy;
March 1997 -
president and CEO, John Edward Curtis Jr. (49), committed
suicide.
1916
- Nathan Handwerker opened nickel hot dog stand on corner of
Surf and Stillwell Avenues in Coney Island, New York; served
Coca Cola (Coca Cola's longest running chain customer);
July 4, 1916 -
hosted first Nathan's Hot Dog Eating Contest (Irish immigrant
James Mullen ate13 hot dogs in buns in 12 minutes; 2007 winner,
Joey Chestnut of San Jose, CA, ate 66 hot dogs and buns in 12
minutes); May 8, 1951
- registered "Nathan's Famous from a HOT-DOG to a national
HABIT" trademark first used January 1, 1915 (potato chips);
July 6, 1955 -
stand sold one millionth hot dog;
1956 - opened second restaurant in Oceanside,
Long Island; 1965 -
opened third restaurant in Yonkers, NY;
1970 - went public; fourth restaurant in
Times Square, New York City; 1975
- acquired Wetsons hamburger chain;
1991 - opened first outlet in airport
(Host Marriott operated newly designed Nathan's kiosk concept at
John F. Kennedy International Airport; now 52 airports served);
1998 - initiated
hot dog branded-product program (food service operators serve
Nathan's hot dogs as branded product on menus - now in more than
900 locations); 1999
- acquired Kenny Rogers Roasters;
2000 -named official hot dog of New York
Yankees.
June 1919
- Roy Allen first brewed root beer in Lodi, CA (based on formula
purchased from pharmacist in Arizona); served it for $.05 at
parade honoring returning World War I veterans; 1922
- took on partner, Frank Wright, employee from original Lodi
location; formally named beverage, A&W Root Beer; started A&W
Restaurants; 1923 - developed, opened nation’s
first car hop service restaurant; 1924 - Allen
bought out Wright, began franchising (America's first franchised
restaurant chain); 1950 - over 450 A&W restaurants
operated nationwide; acquired by Gene Hurtz; formed the A&W Root
Beer Company; one of few nationally established drive-in
restaurant chains; 1960 - over 2,000 A&W
restaurants; 1963 - acquired by J. Hungerford
Smith Company (manufactured A&W Root Beer concentrate since
1921); 1966 - acquired by United Fruit (renamed
United Brands); 1971 - wholly owned subsidiary,
A&W Beverages, Inc., began selling A&W Root Beer at supermarkets
(previously only found at A&W restaurants); 1982 -
A&W Restaurants, Inc. acquired by A. Alfred Taubman, developer
of shopping centers and real estate; October 1993
- A&W brands,
excluding the restaurants, acquired by Cadbury Beverages Inc.;
December 1994 - restaurants acquired by
Sagittarius Acquisitions, Incorporated (headed by former
Executive Vice President of Marketing for Burger King
Corporation); March 1995 - Dr Pepper/Seven-Up
Companies, Inc. acquired by Cadbury Schweppes plc, of London;
A&W root beer became part of renamed Dr Pepper/Seven Up, Inc.
1999 - A&W Restaurants, Inc. acquired Long John
Silver's, Inc.; 2000 - Yorkshire Global
Restaurants, Inc., became parent company;
2002 - acquired by Tricon Global Restaurants, Inc., renamed Yum! Brands, Inc.
 Roy Allen
- A&W Root Beer, Restaurants
(http://www.debbieschlussel.com/archives/royallen.jpg)
Roy Allen
- A&W Root Beer, Restaurants
(http://www.debbieschlussel.com/archives/royallen.jpg)
1921 - Edgar
W. "Billy" Ingram, real estate and insurance agent, borrowed
$700, with partner/cook J. Walter Anderson, opened first White
Castle in Wichita, KS; offered hamburgers at $.05 a piece;
1933 - bought Anderson out; 2005 - more
than 500,000,000 burgers sold; 2006 - more than
380 restaurants.
1922 - Cousins Jack
Kriendler and Charlie Berns opened speakeasy, The Red Head, in
NYC's Greenwich Village to earn tuition for night school (Jack
was a pharmacy student at Fordham; Charlie studied at NYU's
School of Commerce); 1923
- opened second speakeasy, Club Fronton;
1928 - acquired house on West 52nd
Street (previously a bordello owned by Hildegarde Adler), spent
next year converting it to a speakeasy and restaurant;
December 31, 1929/January 1, 1930
- opened "Jack and Charlie's '21' Club" opened at 21 West 52nd
Street in Manhattan; 1931
- model of British Airways "flying boat" was first corporate toy
hung from the '21' ceiling; late
1930s - Jay Van Urk donated first jockey (2004 -
33 jockeys; most recent from Sackatoga Stables representing,
Funny Cide, winner of 2003 Kentucky Derby and Preakness races);
1944 - Humphrey
Bogart and Lauren Bacall get engaged at Table 30;
1985 - acquired by
financier Marshall Cogan; 1995
- acquired by Orient-Express Hotels.
 Jack Kriendler (top) and Charlie Berns
- founded 21 Club
(http://static.orient-express.com/onyc/images/250images/onyc_250_archive7.jpg)
Jack Kriendler (top) and Charlie Berns
- founded 21 Club
(http://static.orient-express.com/onyc/images/250images/onyc_250_archive7.jpg)
1925
- Howard Dearing Johnson (25) inherited small patent medicine
store in Wollaston, MA, and its debts, from his father; bought
ice cream recipe with 2x normal amount of butterfat = sales
soared; 1928 - opened first restaurant;
1929 - opened another restaurant, in downtown
Quincy, MA; 1935 - 25 Howard Johnson's roadside
ice cream, sandwich stands in Massachusetts (through
franchising); became leading tollroad restaurant operator in
country; 1954 - 400 restaurants, entered lodging
industry; opened first franchised motor lodge in Savannah, GA;
1959 - Howard B. Johnson (son) assumed control;
1961 - went public; 1965 - sales
exceeded combined sales of McDonald's, Burger King,
Kentucky Fried Chicken; second largest food feeder in U.S.,
second only to U.S. Army; late 1970s -
over
1,000 restaurants, more than 500 motor lodges;
1980 - acquired
by British conglomerate Imperial Group for more than $630
million dollars; 1985 - acquired for its real
estate by Marriott Corporation (except "Ground Round" restaurant
division); sold motel/hotel/motor lodge system to Prime Motor
Inns (today owned by Cendant Corporation); 2005 -
rights to Howard Johnson name sold to newly-formed La Mancha
Group, LLC.
 Howard Dearing Johnson
(http://www.miltonhistoricalsociety.org/images/HowardDearingJohnson1948.jpg)
Howard Dearing Johnson
(http://www.miltonhistoricalsociety.org/images/HowardDearingJohnson1948.jpg)
1926
- John E. Saxe, Thomas E. Saxe (son) started White Tower
Hamburgers in Milwaukee, WI; considered an imitator of White
Castle (similar white fortress-like structure); mid-1950s
- 230 stores; 1970 - Brock Saxe (grandson) took
over as president of White Tower Management Corporation;
1976 - name changed to Tobrock Corporation.
November 1927
- Ernest Bewley opened Bewley's Cafe in Grafton Street, Dublin,
Ireland (cost £60,000 to build); commissioned renowned artist
Harry Clarke to complete six magnificent stained glass windows
(completed in 1931); largest café and restaurant in Ireland
(over 400 seats, 18,000 square feet).
1933
- Harry and Pasquale (Pat) Olivieri (brothers) made first
version of Philadelphia cheese steak in corner hot dog stand
they founded in 1930 near Italian market in South Philadelphia
(renamed Pat's King of Steaks); piled sliced, grilled beef with
onions on rolls; decades later - Cheez Whiz added to steak and
onions; provalone, American cheese, pizza sauce became options.
December 6, 1933
- Coq d'Or opened, on day Prohibition ended, on first floor of
Drake Hotel (opened in 1920; named for brothers Tracy Drake,
John Drake, developers and proprietors of Blackstone Hotel,
Drake Hotel; acquired property for Drake Hotel from estate of
Potter Palmer in 1916; John Drake [father] had been business
partner of Timothy Blackstone), at the top of Michigan Avenue on
the Magnificent Mile in Chicago, IL; only second bar in town to
obtain liquor license from City of Chicago (first was Berghoff
Restaurant); whiskey at 40 cents a glass.
1934
- Victor Jules Bergeron, Jr., son of waiter at San Francisco's
Fairmont Hotel, owner of grocery store on San Pablo Avenue in
Oakland, CA, used nest egg of $700, carpentry help from his
wife's brothers, his mother's pot-bellied stove and oven, built
small pub across street from store, named Hinky Dink's; served
potent tropical cocktail concoctions, Americanized
adaptations of Polynesian food; create the
world’s first mai tai (short for "mai tai roa ae!" – Tahitian
for "out of this world") - jig of rum, a squeeze of lime, dash
of sugar syrup, splashes of orange Curaçao and French orgeat);
became one of most popular
watering holes in Northern California's Bay Area;
1936 - Herb Caen,
columnist for San Francisco Chronicle, wrote "best restaurant in
San Francisco is in Oakland"; Vic had become "The Trader", Hinky
Dink's became "Trader Vic's", complete with showpiece Chinese
oven; January 7, 1941
- Esther O. Bergeron registered
"Trader Vic's" trademark first used March 1, 1938 (rums);
1944 -
created original Mai Tai, refreshing rum cocktail;
1951 - Trader Vic's
San Francisco opened; eventually opened 25 Polynesian-style
restaurants around world; Lynn Bergeron (son) took over
restaurant operation.
May 1934
- Thomas Andreas Carvelas suffered flat tire on single vending
trailer of frozen custard in Hartsdale, NY, sold out inventory;
first year gross of $3,500; 1936
- developed secret ice-cream formula, freezer model (batch
freezer) - no-air-pump, super-low-temperature ice-cream machine;
introduced the "Buy One Get One Free" offer;
1937 - converted
trailer into frozen custard stand;
1939 - grossed $6,000;
1946 - established two companies: Carvel
Corp. (to make, sell freezers), Carvel Dari-Freeze Stores, Inc.
(to run franchise operation); 1947
- started chain of stores; first retail ice cream shop to
franchise brand; nation’s first retail ice cream franchise; sold
71 freezers at $2,900 each under "Custard King" brand;
December 20, 1949 -
Thomas Carvel of Hartsdale, NY, received a patent for an
"Apparatus for Agitating Dispensing Frozen Foods" ("...for cold
treatment of such foods [frozen custards, ice creams and the
like foods] and for extruding same in semi-solid condition [soft
foods]"); 1951 -
100th store opened; 1952 - 200 Carvel stores, grossed nearly $3
million, operating income of $538,000;
November 2, 1954 - registered "Carvel"
trademark first used in July 1949 (containers made of cardboard
or plastic for the reception of congealed of frozen foods);
1956 - more than
500 stores; one of Big Three of soft-serve ice cream;
1964 - won Federal
Trade Commission, Supreme Court case against franchisees;
1969 - went public;
1973 - revenues of
$27 million; 1978 -
acquired by Tom/Agnes Carvel (went private);
late 1981 - gross
revenues of $180 million, more than 8,000 employees;
1985 - 865
franchise stores, revenues of $300 million;
1989 - 90% Carvel interest acquired by
Investcorp (Bahrain) for about $80 million; 700 stores,
third-largest ice-cream operation in United States;
1998 - sales of
about $200 million ($95 million from supermarkets);
1999 - franchise
stores down to 400, retail presence in 4,500 supermarkets;
2001 - acquired by
Roark Capital (Atlanta, GA).
 Thomas Andreas Carvelas
(Tom Carvel) - Carvel Ice Cream
(http://www.carvel90210.com/images/tomcarvel.gif?nxg_versionuid=published)
Thomas Andreas Carvelas
(Tom Carvel) - Carvel Ice Cream
(http://www.carvel90210.com/images/tomcarvel.gif?nxg_versionuid=published)
Mid 1930s
- Howard D. Johnson acquired Wayland Red Coach Grill Restaurant;
created chain of upscale luxury dining facilities based on
pre-Revolutionary American post house theme; featured
red-shingled roof, log siding exterior, two massive fieldstone
fireplaces, accurate reproduction Colonial fixtures and
furnishings inside; August 28, 1962
- Tally Ho Grill of Boston, Inc. registered "Red Coach Grill"
trademark first used in 1934 (restaurant services);
early 1980s -
Imperial Group Ltd. (Howard Johnson Company parent) closed
chain.
1935 - Prestley
Blake (20) and Curtis Blake (18) co-founded Friendly Ice Cream shop in Springfield, MA with
$547 borrowed from their parents; double dip cones for $0.05;
1940 - added food
to ice cream menu (hamburger); 1951
- operated 10 Friendly Restaurants in Western Massachusetts,
Connecticut; October 19, 1954
- Friendly Ice Cream Corporation registered "Friendly Ice Cream"
trademark first used July 18, 1935 (ice cream);
1974 - chain of 500
restaurants concentrated in Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern U.S.;
1979 - acquired by
Hershey Foods Corporation; September 1988 - acquired by Donald
N. Smith (Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer of
The Restaurant Company); 1989
- added "s" to name ("Friendly’s");
2001 - Blake began 7-year, $11 million
dollar successful legal fight for control of company with Donald
N. Smith (former Friendly’s CEO; didn’t like debt Friendly’s had
incurred, Smith’s strategy of closing, selling restaurants to
pay down debt; didn’t like relationship between Friendly’s and
Perkins, another restaurant company Smith controlled, Smith’s
use of corporate jet); August 2007
- Friendly’s acquired by affiliate of Sun Capital partners, Inc.
leading private investment firm;
2011 - more than 500 Friendly’s restaurants,
sales of $700 million, distribution through more than 6,500
retail locations; October 5, 2011
- filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection (roughly 10,000
employees, more than 400 restaurants known for sundaes and
hamburgers).

Curtis and
Prestley Blake - Friendly's
(http://www.boston.com/business/ticker/PrestleyBlake.jpg)
1936 - Bob
Wian sold his car for $350.00, opened small restaurant in
Glendale, CA called called Bob’s Pantry; 1938 -
name changed to Bob's Big Boy; 1940s - franchised
the concept; May 19, 1953 - Robert C. Wian
Enterprises, Inc. registered "Big Boy" trademark first used in
December 1947 (hamburger sandwiches); "double-deck" hamburger
named for happy, chubby youngster (about 6) who came into
restaurant; 1967 - acquired by Marriott Corp. for
$7 million; 1987 - acquired by Fred, Louis, John
Elias, one of larger franchise operators (since 1951);
2000 - declared bankruptcy; 2001 -
acquired by Robert Liggett Jr., former radio station operator
(Liggett Broadcast Group); formed "Big Boy Restaurants,
LLC".
July 13, 1937 - Vernon Carver Rudolph
made, sold first Krispy Kreme doughnuts at shop in
Winston-Salem, NC (based on secret yeast-raised doughnut recipe
acquired in 1933 from French chef from New Orleans);
March 13, 1951 -
Krispy Kreme Doughnut Company registered "Krispy Kreme"
trademark first used in August 1934 (doughnuts and the mix for
making same); 1962
- developed method to extrude by air pressure from dough hopper
to trays of continuous proof box to form perfect doughnut shape;
May 28, 1976 -
acquired by Beatrice Foods Company;
February 28, 1982 - acquired by group of
franchisees; April 2000
- went public; 2003
- stock price near $50 (adjusted for splits), nearly 400 Krispy
Kreme stores produced nearly 3 billion doughnuts/year.
August 4, 1938
- Sherb Noble ran "All the Ice Cream You Can Eat for 10 Cents''
special" at Herb's, walk-in ice cream store in Kankakee, IL;
featured soft frozen dairy product (soft-serve ice cream)
created by J. F. ``Grandpa'' McCullough (67) and Alex (40, son)
in ice-cream mix plant business in Green River, IL; dished out
more than 1,600 servings of new dessert in 2 hours; June
22, 1940 - Noble opened first Dairy Queen store in
Joliet, IL; triple-decker cone was a nickel, sundae sold for 8
cents; 1941 - McCulloughs opened second store in
Moline, IL; December 1941 - fewer than 10 Dairy
Queen stores; 1947 - 100 stores; 1950
- 1,446 stores; 1955 - 2,600 stores; March
13, 1962 - McCullough's Dairy Queen registered "Dairy
Queen" trademark first used June 1940 (Machine for Freezing and
Dispensing a Semi-Frozen Dairy Product); 1962 -
group of territory operators formed International Dairy Queen
Inc.; Hugh McCullough (Alex's son) sold stake for $1.5 million;
January 1998 - acquired by Berkshire Hathaway
Inc.; 2007 - more than 5,900 restaurants in United
States, Canada, 20 foreign countries.
1940 -
Colonel Harlan Sanders created Original Kentucky Fried Chicken
Recipe (made honorary Colonel by Kentucky Governor Ruby Laffoon
in 1936 in recognition of his contributions to state's cuisine);
1952 - awarded Pete Harman of Salt Lake City with
first KFC franchise; handshake agreement stipulated payment of
nickel to Sanders for each chicken sold; 1957 -
Kentucky Fried Chicken first sold in buckets; 1960
- 190 KFC franchisees, 400 franchise units in U.S. and Canada;
1964 - Sanders sold his interest in U.S. company
for $2 million to a group of investors headed by John Y. Brown
Jr., future governor of Kentucky; remained public spokesman for
company; August 23, 1966
- Kentucky Fried Chicken Corporation registered "Colonel
Sanders' Recipe Kentucky Fried Chicken" trademark first used
December 1950 (fresh prepared chicken and gravy, packaged and
sole in retail trade, prepared potatoes, chicken parts,
biscuits, baked beans, barbecue, and salads); 1971 -
more than 3,500 franchised,
company-owned restaurants worldwide; acquired by Heublein Inc.
January 16, 1945
- Carl (28) and Margaret Karcher opened
full-service restaurant, Carl’s Drive-In Barbeque, in Anaheim,
CA (had owned, operated hot dog carts since 1941); 1946
- added hamburgers to menu; 1956 - opened first
two Carl’s Jr.® restaurants (junior versions of Carl’s original
drive-in restaurant) in Anaheim, nearby Brea; 1966
- incorporated Carl Karcher Enterprises, Inc.;
October 20, 1970 -
Carl Karcher Enterprises, Inc. registered "Carl's Jr."
trademark first used February 1964 (restaurant services); 1975
- more than 100 Carl’s Jr. locations in Southern California;
America's fourth largest burger chain; 1977 -
first quick-service chain to offer salad bars in all 200
locations; 1979 - sales exceeded the $100 million;
1981 - 300 restaurants in operation, went public;
1989 - sales topped $480 million at 534
restaurants; 1994 - became wholly-owned subsidiary
of CKE Restaurants, Inc.; 1997 - acquired Hardee's
Food Systems; 2006 -sales of $1.52 billion, 29,000
employees.
 Carl Karcher
- CKE Restaurants, Inc.
(http://www.nndb.com/people/691/000025616/carlkarcherbig.jpg)
Carl Karcher
- CKE Restaurants, Inc.
(http://www.nndb.com/people/691/000025616/carlkarcherbig.jpg)
1945
- Irvine Robbins opened the Snowbird Ice Cream Store in
Glendale, CA; 1946
- Burton Baskin, brother-in-law, joined Robbins to found
Baskin-Robbins; 1953
- big "31" sign made its debut at all Baskin-Robbins
stores, offered customers a different ice cream for every day of
the month; March 14, 1961
- Huntington Ice Cream Company (doing business as Baskin-Robbins
Ice Cream Corporation) registered "Baskin-Robbins 31 Ice Cream"
trademark first used September 23, 1953 (confections, namely ice
cream); 1973 -
acquired by J. Lyons & Co.; 1978 - acquired by Allied Domecq.
 Irvine Robbins
- co-founder Baskin-Robbins
(http://www.glendalehistorical.org/images/robbins.gif)
Irvine Robbins
- co-founder Baskin-Robbins
(http://www.glendalehistorical.org/images/robbins.gif)
1946
- Dave
Barham opened first Hot Dog on a Stick at Muscle Beach, Santa
Monica, CA; 1990 - 60 stores operating in 12
states; 2006 - 105 company-owned U.S. locations
plus 25 franchised units; 100% owned and operated by its
employees.
1946 - Arthur J.
Preston opened Preston's Candy & Ice Cream in Burlingame, CA;
winner of many international awards, including Grand Champion
Medallion of International Truffle Competition for three years
in a row, numerous awards in the Retail Confectioners
International competition.
1948 - Esther
and Harry Snyder founded In-N-Out Burgers, West Coast
drive-through chain, in Baldwin park, CA (same year as McDonald
brothers opened first limited-menu fast-food restaurant in San
Bernadino, CA, 43 miles away); strategy: limited menu choices,
fresh food, deliberately slow growth (202 restaurants, $350
million annual sales vs. 31,886 restaurants, $20.4 billion
annual sales for McDonalds);
October 21, 1975 - In-N-Out Burgers Corporation
registered "In-N-Out Burgers" trademark first used February 1960
(restaurant services and carry-out restaurant services).
December 12, 1948
- Richard and Maurice McDonald opened drive -in restaurant in
San Bernardino, CA; featured hamburgers (15 cents), french fries
(10 cents), fast service (Speedee Service
System); 1955 -
exclusive McDonald's
franchising
acquired by Ray Kroc.
1950
- William Rosenberg changed name of "Open
Kettle" restaurant in Quincy, MA (founded 1948) to Dunkin'
Donuts; 1955 - first franchise established in
Worcester, MA; February 2, 1960 -
Dunkin' Donuts of America, Inc. registered
"Dunkin' Donuts" trademark first used in May 1952 (doughnuts and
doughnut flour, fruit fillings for doughnuts, cookies, cakes and
pies, vegetable oil shortening and coffee); 1963 -
100th opened; 1979 - 1000th opened; 1982
- Fred the Baker, "Time to Make the Donuts" television campaign
began; 1990 - acquired by Allied Domecq PLC;
1995 - 1000th international shop opened; 2000
- opened 2000th shop worldwide; 2005 -
Pernod Ricard,
Fortune Brands
acquired Allied Domecq $14.2 billion; December 14, 2005
- Thomas H. Lee Partners, Carlyle Group, Bain Capital announced
definitive agreement to acquire Dunkin' Brands Inc. from Pernod
Ricard SA $2.425 billion (12.8 times cash flow); number one
retailer of coffee-by-the-cup in America (nearly one billion
cups a year); largest coffee, baked goods chain in world (more
than 6,500 shops in 29 countries); 2006 -
worldwide system sales - $6.4 billion.
 William Rosenberg -
Dunkin' Donuts
(http://www.dunkindonuts.com/content/dunkindonuts/en/company/
founder/_jcr_content/centerPar/feature/image.img.jpg/1292018897289.jpg)
William Rosenberg -
Dunkin' Donuts
(http://www.dunkindonuts.com/content/dunkindonuts/en/company/
founder/_jcr_content/centerPar/feature/image.img.jpg/1292018897289.jpg)
October 1950 -
Marilyn and Harry Lewis opened Sunset Strip cafe; evolved into
Hamburger Hamlet, string of show-biz-themed,
carpet-and-chandelier grills in upper-midscale market;
1969 - went public; 1988 - 24-unit chain
(1987 sales of sales of $44.8 million) acquired by Weatherly
Private Capital Inc. for $33 million; December 6, 1995
- filed for bankruptcy protection; 1997 - 14
restaurants acquired by Koo Koo Roo, Inc. for$11.45 million;
1998 - Koo Koo Roo Enterprises, Family Restaurant
Group, Restaurant Enterprises Group Inc. merged, formed Prandium
Inc.; May 2002 - filed for bankruptcy protection;
July 2002 - emerged from bankruptcy; October
8, 2003 - filed for bankruptcy; 2004 -
12-unit Hamlet Group chain acquired by Andrew Tavakoli for $10
million.
1951 - Robert O. Peterson
founded Jack In The Box; hamburgers with speed, convenience of
the automobile; American Drive-Through; first modern, fast-food,
limited menu, cash-only restaurant.
1953
- Bob Evans formed Bob Evans Farms Inc. with five friends,
relatives; 1962 - first restaurant, The Sausage
Shop, 12-stool diner in Gallipolis, OH; September 2, 1969
- Bob Evans Farms, Inc. registered "Bob Evans Farms" trademark
first used September 15, 1964 (smoked sausage and smoke pork
sausage); 2006 -
sales of $1.7 billion, 579 restaurants in 18 states.
 Bob Evans - Bob
Evans Farms
(hhttp://www.bobevans.com/resources/uploaded/Our%20Company/History%20and%20Legacy/Bob%20Evans.jpg)
Bob Evans - Bob
Evans Farms
(hhttp://www.bobevans.com/resources/uploaded/Our%20Company/History%20and%20Legacy/Bob%20Evans.jpg)
1953 - Troy Smith,
partner opened Top Hat root beer stand (profit margins were four
times greater), Log House Restaurant in Shawnee, OK;
1955 - Smith ended
partnership, got out of Log House Restaurant; focused on turning
Top Hat root beer stand into successful drive-in concept;
pioneered use of angled, covered parking, intercom speaker
system that allowed customers to place orders from their
cars; “Service With the Speed of Sound” - tagline for Top Hat;
concept took off; drive-in located in Stillwater, OK first Top
Hat to adopt fledgling chain’s new name of Sonic ('speed of
sound'); 2009 -
nearly 3,600 Sonic Drive-Ins located in 42 states.
1953 - Harold
Butler opened Danny's Donuts in Lakewood, CA; 1954
- renamed Danny's Coffee Shops; 1959 - renamed
Denny’s Restaurants (sued by Coffee Dan's chain over brand-name
similarity), with 20 Denny’s serving customers by year’s end.
1954 - James
McLamore, David Edgerton founded Burger King Corporation in
Miami, FL; hamburger cost 18¢; 1957 - WHOPPER®
sandwich introduced, cost 37¢; 1961 - operated 45
restaurants throughout Florida, Southeast; McLamore
and Edgerton acquired national franchise rights for the Company;
October 3, 1961 -
Burger King of Florida, Inc. registered "Burger King: trademark
first used July 28, 1953 (drive-in restaurant services).
April 15, 1955
- Ray Kroc opened first franchised McDonald's in Des Plaines, IL
after having bought exclusive franchising rights from
Richard and Maurice
McDonald of San Bernadino, CA (first day's sales: $366.12);
1961 - 228 McDonald's franchises, generated
$37 million in gross profits;
bought out McDonald
brothers for $2.7 million;
1963 -
Ronald McDonald made debut as corporate spokesclown;
January 8, 1963 -
McDonald's Self-Service System registered "McDonald's" trademark
first used December 1948 (drive-in restaurant services);
1965 -
went public at $22.50 a share; split 12 times
in next 35 years;
1975 -
first drive-through window;
2000
- sales in U.S. peaked at average of
$1.6 million/year/per rfestaurant.
1957 - Dan Carney
read article from Saturday Evening Post about pizza fad on
college campuses, shown to him by landlady of Carney family's
grocery store and small beer bar next door (she wanted to
get out of bar business); June 15, 1958
- Dan and Frank Carney borrowed $600 from their mother,
remodeled tavern next door to family market, opened first Pizza
Hut in Wichita, KS; first sign had room for only nine letters,
including "pizza"; chose "hut" because facility shaped like one;
1959 - five stores,
310 stores in first decade; April
10, 1962 - Pizza Hut, Inc. registered "Pizza
Hut" trademark first used September 1, 1958 (restaurant
services); 1964 -
basic free-standing design of standardized Pizza Hut restaurants
opened; 1977 -
3,400 domestic and international stores; acquired by PepsiCo.
for $300 million; 1997
- spun off into Tricon; May 16,
2002 - Tricon officially became YUM! Brands.
 Frank and Dan Carney
- Co-Founders Pizza Hut
(http://webs.wichita.edu/depttools/depttoolsmemberfiles/shockermag/18/carneys.jpg)
Frank and Dan Carney
- Co-Founders Pizza Hut
(http://webs.wichita.edu/depttools/depttoolsmemberfiles/shockermag/18/carneys.jpg)
July 7, 1958 - Al
and Jerome Lapin, early investors Albert and Trudy Kallis opened
first International House of Pancakes in Toluca Lake, CA;
1960 - began
expansion through franchising; 1961
- went public; 1963
- adopted name International Industries;
March 23, 1965 - International
Industries, Inc. registered "International House of Pancakes"
trademark first used February 26, 1960 (restaurant services);
1973 - introduced
IHOP acronym; July 16, 1974
- International Industries, Inc. registered "IHOP" trademark
first used November 1972 (restaurant services);
1992 - 500th IHOP
opened; 1993 -
average sales per IHOP exceeded $1 million;
1998 - system wide sales exceeded $1
billion; 2001 -
1,000th IHOP opened; July 16, 2007
- said it would pay $1.9 billion for Applebee's International,
casual dining chain of restaurants.
 Al Lapin
- founder IHOP
(http://image2.findagrave.com/photos250/photos/2006/309/8960296_116285644612.jpg)
Al Lapin
- founder IHOP
(http://image2.findagrave.com/photos250/photos/2006/309/8960296_116285644612.jpg)
1958 - David
Tallichet opened The Reef, South Seas-inspired waterfront
restaurant, on edge of harbor in Long Beach, CA; pioneered theme
restaurants, founded multi-concept restaurant company, Specialty
Restaurants Corp.; 1968
- went public; 1980
- sales peaked at $180 million; went private;
1993 - filed
Chapter 11 bankruptcy (operated 50 restaurants);
2007 - operated 25
restaurants.
August 22,
1958 - Ben and Virginia Ali opened Ben's Chili
Bowl on U St. ("Black Broadway") in Washington, DC; used $5,000,
renovated 1909 building (former Minnehaha Theater); frequented
by Duke Ellington, Miles Davis, Bessie Smith, Ella Fitzgerald,
Cab Calloway, Nat King Cole, Redd Foxx, Dick Gregory, Martin
Luther King Jr., Bill Cosby; May
2001 - Ben and Virginia inducted into DC Hall of
Fame.
 Ben Ali
- Ben's Chili Bowl
(http://www.roadfood.com/photos/3216.JPG)
Ben Ali
- Ben's Chili Bowl
(http://www.roadfood.com/photos/3216.JPG)
July 1959 - Jerry
Brody, CEO of Restaurant Associates, Joseph Baum, head of
Restaurant Associates Industries's specialty restaurant
division, opened Four Seasons Restaurant (named after a haiku
collection) in Seagram's Building; $4.5 million project in the
Seagram Building with interior design by Philip Johnson,
artworks by Miro and Picasso; five dining rooms seated 400,
employed 20 captains, 50 waiters, 15 busboys;
1972 - acquired for
$230,000 by Tom Margittai, Restaurant Associates Vice President,
and Paul Kovi, Four Seasons director (1973 sales of $2 million);
1984 - $12 million
annual sales; October 1989
- first Manhattan restaurant to achieve landmark status;
1995 - acquired by
Joseph W. Seagram Company.
1960 - Tom and
James Monaghan
borrowed $500, bought "Domi-Nick's," pizza
store in Ypsilanti, MI; 1961
- James traded his half of business to Tom for Volkswagen
Beetle; 1965 - Tom
Monaghan sole owner of company, renamed "Domino's
Pizza, Inc." 1967 -
opened first Domino's Pizza franchise store in Ypsilanti, MI;
1968 - opened first
Domino's store outside of Michigan, in Burlington, VT;
1978 - opened 200th
Domino's store; August 25, 1981 -
Domino's Pizza, Inc. registered "Domino's Pizza" trademark first
used February 1965 (Rendering Technical Assistance in the
Establishment and Operation of Stores Exclusively Engaged in the
Baking and Delivering of Hot Pizza Pies Made to Order for
Consumption Off the Premises); 1983
- 1,000th Domino's store opened;
1985 - opened 954 units, total of 2,841;
fastest-growing pizza company in country;
1989 - opened
5,000th store; 1990
- signed 1,000th franchise; 1998
- Monaghan retired, sold 93% of Company to Bain Capital, Inc.;
1999 - worldwide
sales exceeded $3.36 billion; 2012
- opened 10,000 store in Istanbul, Turkey.
September 3, 1960 -
Wilbur Hardee founded Hardee's restaurant chain with drive-in
hamburger stand near East Carolina University campus in
Greenville, NC; no tables, no waiters, 15-cent fresh-ground,
lean beef burger made to order on custom-build charcoal broiler;
May 5, 1961 - Jim
Gardner, Leonard Rawl to opened first Hardee's franchise
restaurant in Rocky Mount, NC;
November 20, 1962 - Hardee's Food Systems, Inc.
registered "Hardee's" trademark first used October 21, 1961
(restaurant services); 1963
- went public; introduced pagoda-style building; Hardee lost 51%
controlling interest in company in card game with Gardener,
Rawl; sold remaining stake for $37,000;
March 8, 1966 - Hardee's food Systems,
Inc. registered "Hardee's L'il Chef" trademark first used April
7, 1963 (restaurant services); 1981
- acquired by Imasco Ltd. (Canadaian conglomerate); became
nation's fourth-largest burger quick-service restaurant chain;
1997 - acquired by
Carl's, Jr. (became CKE Restaurants, Inc.);
2008 - 1,900 Hardee's across Midwest,
Southeast, 200 international locations.
 Wilbur Hardee
- Hardee's Food Systems
(http://msnbcmedia.msn.com/j/msnbc/components/photo_storylevel/080623/080623-obit-hardee-vsmall5p.rp98x98.jpg) Wilbur Hardee
- Hardee's Food Systems
(http://msnbcmedia.msn.com/j/msnbc/components/photo_storylevel/080623/080623-obit-hardee-vsmall5p.rp98x98.jpg)
April 21, 1962 -
President John F. Kennedy opened "Top of the Needle" in
Seattle, WA, by remote control from Palm Beach, FL; first
revolving restasurant in U.S. (originally called "Eye of the
Needle", on top of "The Space Cage"); unmatched in its 360°
panoramic view of Seattle skyline, Puget Sound;
2000 - re-opened as
SkyCity, larger restaurant, rotated 360 degrees in exactly 47
minutes.
1964 - Tim
Horton, legend in National Hockey League, sold first Tim Hortons
franchise, on Ottawa Street in Hamilton, ON, to Ron Joyce,
former police officer; offered only two products – coffee,
donuts; 1967 - Joyce became full partner;
1975 - Joyce became sole owner (Horton died in traffic
accident); 40 stores; 1976 - introduced Timbit
(bite-sized donut hole); grew into largest quick service
restaurant chain in Canada; January
4, 1983 - Tim Donut Limited registered "Tim
Horton" trademark (restaurant and take-out services); February 1987 - opened
300th store in Calgary, AB; 1995 - merged with
Wendy’s International, Inc.; 95% franchise owned, operated;
1997 - 1500th store opened in Pickerington, OH;
December 2000 - 2000th store opened in Toronto, ON;
September 29, 2006 - spun off as a separate
company; December 2006 - 3000th store opened in
Orchard Park, NY.
 Ron Joyce, Tim Horton
- Tim Hortons
(http://www.timhortons.com/ca/images/general/history1967.jpg)
Ron Joyce, Tim Horton
- Tim Hortons
(http://www.timhortons.com/ca/images/general/history1967.jpg)
January 15, 1964
- Elmer Valentine, former Chicago police officer, invested
$20,000 of partnership profits from P.J.'s nightclub, opened
Whiskey a Go Go in a bank building on the northwest corner of
Sunset Boulevard and Clark Street in West Hollywood, CA;
patterned after Whiskey a Go Go discotheque in Paris, became
musical legend of 1960s; introduced go-go girl suspended in
cage; Doors (with Jim Morrison) were house band; signed Johnny
Rivers (21) to one-year contract; opened satellite branches in
San Francisco, Atlanta; 1990s
- sold his interest.
July 23, 1964
- Leroy and Forrest Raffel opened Arby's (R.B.,
initials of Raffel Brothers) Roast Beef Restaurant in Boardman,
OH; January 4, 1966
- Arby's Inc. registered "Arby's Roast beef sandwich Is
Delicious" trademark first used November 20, 1961 (restaurant
services); 1970s -
added average of 50 restaurants a year;
1981 - opened 1,000th restaurant;
1993 - acquired by
Triarc Companies, Inc.; July 25,
2005 - Triarc acquired RTM Restaurant Group,
Arby's largest franchisee, formed Arby's Restaurant Group, Inc.
(more than 3,500 restaurants.
 Leroy and Forrest Raffel
- founders Arby's
(http://arbys.com/desktop/images/about/company-history/photos/1964.jpg)
Leroy and Forrest Raffel
- founders Arby's
(http://arbys.com/desktop/images/about/company-history/photos/1964.jpg)
1965
- Ruth Fertel, divorced mother raising two sons, mortgaged her
New Orleans home for $22,000, bought Chris's Steak House;
renamed it Ruth's Chris Steak House;
1976 - original Ruth's Chris Steak House
destroyed in a fire; 1977
- opened second restaurant in Metairie, LA; granted first
franchise for a Ruth's Chris Steak House in Baton Rouge;
July 31, 1979 -
Ruth's Chris Steak House, Inc. registered "Ruth's Chris"
trademark first used in 1973 (restaurant and lounge servcies);
1999 - acquired for
$160 million by private equity firm;
August 9, 2005 - IPO gave company market
capitalization of $400 million.
August 14, 1956 - Federal Nut Co., Inc.
registered "Chock Full O' Nuts-The Heavenly Coffee" trademark
first used July 1, 1953 (coffee).
1966 - Norm
Brinker founded Steak & Ale restaurants; 1976 - acquired
by Pillsbury; 1983 - bought Chili's; 1990
- renamed Brinker International.
1967
- Jim Delligatti,
Uniontown, PA McDonald's franchisee (one of Ray Kroc's earliest
franchisees) introduced Big Mac; added lettuce, cheese, pickles,
onions, and most important, the "special sauce," to create one
of world's best-known hamburgers;
1968 - offered throughout
McDonald's system;
July 30, 1974 -
registered "Big Mac" trademark January 1, 1971 (specially
prepared carry-out type foods).
1968 - Bill Darden opened first Red Lobster in
Lakeland, FL; 1995 - together with Olive Garden, Bahama Breeze became part of Darden Restaurants; 2007
- close to 700 Red Lobster locations in United States, Canada.
November 15, 1969
- Dave Thomas opened first Wendy's Old-Fashioned Hamburgers
outlet in downtown Columbus, OH; named for 8-year-olld daughter,
Melinda Lo, nicknamed, Wendy; April
6, 1971 - Wendy's Old Fashioned Foods, Inc.
registered "Wendy's" trademark first used November 15, 1969
(restaurant services and carryout restaurant services); August 1972 - first
franchise sold; March 2, 2007 - original restaurant closed.
August 28, 1971 - Alice Waters opened Chez Panisse Restaurant in Berkeley, CA; started an organic food
movement.
1973 -
McDonald's
introduced Egg McMuffin; created by Herb Peterson (operated
Santa Barbara McDonald's); used teflon-coated ring to make round
eggs.
1979 -
McDonald's
introduced Happy Meal; created by Bob Charles, Colorado
franchisee); added toy to children's orders.
1979 - Tim
and Nina Zagat published 2-page typed list of New York
restaurants compiled from reviews from friends; delivered to
bookstores which would stock it; 2000 - third of
company acquired by investment group led by General Atlantic
Partners (valued company qt $100 million); 2007 -
sold 5.5 million guides in more than 100 countries, 1.5 million
registered web site users.
February 1982 - Austrian-born Wolfgang
Puck opened Spago (Italian for string) on Sunset Strip in West
Hollywood to serve simple, fresh, innovative food by skilled,
friendly staff in casually sophisticated yet comfortable
environment (former part owner of Ma Maison, magnet for
Hollywood's rich and famous); first signature dish, gourmet
pizza topped with smoked salmon and caviar, put restaurant Los
Angeles foodie map; 1986
- regularly featured guest on ABC's "Good Morning America";
1990 - Spgao
grossing $6 million per year; 1997
- Spago Beverly Hills opened; 2000
- Emmy-winning television series, "Wolfgang Puck," debuted on
Food Network (aired for five seasons).
 Wolfgang Puck
- Spago
(http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/ed/
Oscar_Official_Chef_Wolfgang_Puck.jpg/220px-Oscar_Official_Chef_Wolfgang_Puck.jpg)
Wolfgang Puck
- Spago
(http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/ed/
Oscar_Official_Chef_Wolfgang_Puck.jpg/220px-Oscar_Official_Chef_Wolfgang_Puck.jpg)
March 2, 1984
- first McDonald's franchise closed -- in Des Plaines, IL.
June 6, 1986 - Ronn
Teitelbaum opened first Johnny Rockets on Melrose Avenue, Los
Angeles; June 3, 2005
- 175th restaurant opened in Hicksville, New York.
January 31, 1990
-
McDonald's Corp. opened first fast-food
restaurant in Moscow; throngs lined up to pay equivalent of
several days' wages for Big Macs, shakes, french fries.
April 10, 1991 - Last automat (coin operated
cafeteria) closes (3rd and 42nd St, New York City).
April 23,
1992 - McDonald's opened its first restaurant in
Beijing.
December 7, 2006
- Rank Group PLC agreed to sell Hard Rock cafes, including
massive collection of rock 'n' roll memorabilia, for $965
million to Seminole Tribe of Florida (124 Hard Rock Cafes, four
Hard Rock Hotels, two Hard Rock Casino Hotels, two Hard Rock
Live! concert venues, stakes in three unbranded hotels);
Seminoles own, operate five other casinos in Florida; 90
percent of the tribe's budget comes from gaming revenue.
March 30, 2008
- Restaurant traffic does not always fall during a recession
(NPD Group):
 (http://graphics8.nytimes.com/images/2008/03/30/business/
20080330_COUNT_GRAPHIC.jpg)
(http://graphics8.nytimes.com/images/2008/03/30/business/
20080330_COUNT_GRAPHIC.jpg)
April 24, 2008
- Wendy's International Inc. signed $2.3 billion merger
agreement with Triarc Companies Inc., franchisers of Arby's
restaurant system; created third largest quick-service
restaurant chain in U.S., with approximately $12.5 billion in
annual sales, more than 10,000 units; Triarc changed name to
incorporate Wendy's.
(21 Club), H. Peter Kriendler with H. Paul
Jeffers (1999).
"21": Every Day Was New Year's Eve: Memoirs of a Saloon Keeper
(Dallas, TX: Taylor Publ. Co., 282 p.). Younger Brother of Jack
Kriendler, co-founder. 21 (Restaurant : New York)--History;
Cookery; Restaurants--New York (State)--New York.
(A.P.V. Company), G. A. Dummett (1981).
From Little Acorns: A History of the A.P.V. Company Limited.
(London,UK: Hutchinson Benham, 247 p.). A.P.V. Company--History;
Food processing machinery industry--Great Britain--History;
Chemical plant equipment industry--Great Britain--History.
(All American Hot Dog Company), Louis Di
Raimondo, John C. Havens (2004).
I'm On A Roll: America's Celebrity Hot Dog King, Louie Di
Raimondo. (Bloomington, IN: AuthorHouse, 116 p.).
Founder and President of the All American Hot Dog Company. Di
Raimondo, Louis; Hot dog stands--Florida--Miami.
(Arby's), Whit Smyth (1999).
Great Taste Endures: 35 Years of Success: The Story of Arby's
Restaurants. (New York,. NY: Lebhar-Friedman Books, 126
p.). Raffel, Leroy; Raffel, Forrest; Arby's, Inc.--History;
Franchises (Retail trade); Restaurateurs--United States.
(Baker Perkins Holdings Ltd.), Augustus Muir
(1968).
The History of Baker Perkins. (Cambridge, UK: Heffer,
214 p.). Baker Perkins Holdings, ltd.; Restaurant Supplies;
Restaurants and Foodservice; Food and Beverage.
(Barjo Restaurant), J. Emily Foster (2001).
The Legend of Barjo Restaurant: The Life of Josephine McAllister
Stone. (Lisbon Falls, ME: Soleil Press, 416 p.). Stone,
Josephine McAllister, 1903- ;
Restaurateurs--Maine--Norway--Biography; Family--Maine;
Women--Biography; Norway (Me.)--History.
(Benihana), Jack McCallum (1985).
Making It in America: The Life and Times of Rocky Aoki,
Benihana's Pioneer. (New York, NY: Dodd, Mead, 165 p.).
Aoki, Rocky, 1938- ;Restaurateurs--United States--Biography.
(Ben’s Chili Bowl), Tracey Gold Bennett, Nizam
Ben Ali (2008).
Ben’s Chili Bowl: 50 years of a Washington, D.C. Landmark.
(Charleston, SC: Arcadia Pub.. 128 p.). Son of founder. Ben’s
Chili Bowl; Ali, Virginia and Ben; Restaurants -- Washington,
DC. August 22, 1958 - West Indian
immigrant Mahaboob Ben Ali, Virginia Rollins (fiancée) opened
hot dog, chili shop on U Street in Washington, DC; 50-year
history of Ben’s Chili Bowl, U Street, Ali family, patrons.
(Le Bernardin), Eric Ripert, Christine Muhlke (2008).
On the Line. (New York, NY: Artisan, 240 p.). Chef of
Manhattan seafood mecca Le Bernardin. Le Bernardin (Restaurant);
Restaurant management. How does 4-star restaurant stay on top
for more than two decades? Behind scenes at Le Bernardin, one of
just three New York City restaurants to earn three Michelin
stars; business of haute cuisine; how kitchen organized;
real cost of food, fierce discipline to achieve culinary
perfection on plate almost 150,000 times a year.
(Bewley's Cafés Limited), Fiona Murdoch
(2002).
Victor Bewley's Memoirs. (Dublin, IR: Veritas
Publications, 112 p.). Bewley, Victor; Bewley's Cafés Limited;
Restaurateurs--Ireland--Biography; Quakers--Ireland--Biography.
(Billy Goat Inn), Rick Kogan (2006).
A Chicago Tavern A Goat, a Curse, and the American Dream.
(Chicago, IL: Lake Claremont Press, 115 p.). Sianis, William
--Biography --Anecdotes; Sianis, Sam, 1935- --Biography
--Anecdotes; Kogan, Rick --Homes and haunts --Illinois --Chicago
--Anecdotes; Billy Goat Tavern (Chicago, Ill.) --History --20th
century --Anecdotes; Chicago Cubs (Baseball team) --History
--20th century --Anecdotes; Bars (Drinking establishments)
--Illinois --Chicago --Anecdotes; Greek Americans --Illinois
--Chicago --Biography --Anecdotes; Chicago (Ill.) --Social life
and customs --20th century --Anecdotes; Chicago (Ill.)
--Biography --Anecdotes. Summer of 1934 - baby goat fell off truck, limped into tavern owned by Greek immigrant William Sianis;
became Chicago icon; haven for newspaper reporters, policemen, politicians,
else drawn to hospitality, showmanship of Sianis.
(Blanchard's Restaurant), Bob and Melinda
Blanchard (2005).
Live What You Love: Notes from an Unusual Life. (New
York, NY: Sterling Pub., 216 p.). Owners, Blanchard's Restaurant
(Anguilla). Blanchard, Robert, 1951- ; Blanchard, Melinda, 1952-
; Entrepreneurs--United States--Biography;
Entrepreneurs--Anguilla--Biography;
Restaurateurs--Anguilla--Biography; Conduct of life;
Vermont--Biography; Anguilla--Biography.
(Blimpie), Tony Conza (2000).
Success, It's a Beautiful Thing: Lessons on Life and Business
from the Founder of Blimpie International (New York, NY:
Wiley, 256 p.). Founder, Blimpie International. Conza, Tony;
Success in business; Businessmen -- United States -- Biography;
Restaurateurs -- United States -- Biography.
(Boost), James Kirby (2005).
Janine Allis: Business Secrets of the Woman Behind Boost Juice.
(Milton, Queensland: Wiley, 125 p.). Allis, Janine, 1965- ;
Boost (Firm)--History; Fast food restaurants--Australia;
Businesswomen--Australia--Biography; Franchises (Retail
trade)--Australia; Success in business--Australia.
(Brinker International), Norman Brinker and
Donald T. Phillips (1996).
On The Brink: The Life and Leadership of Norman Brinker.
(Arlington, TX: Summit Publishing Group, 203 p.). Restaurateur.
Norman Brinker, Restaurants.
(Burger King), James W. McLamore (1998).
The Burger King: Jim McLamore and the Building of an Empire.
(New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 286 p.). McLamore, James W.,
1926-1996; Burger King Corporation; Restaurateurs--United
States--Biography.
 James W. McLamore
(left) - co-founder Burger King
(http://www.uvag.de/_data/burgerking.jpg) James W. McLamore
(left) - co-founder Burger King
(http://www.uvag.de/_data/burgerking.jpg)
(Carnegie Deli), Milton Parker, Allyn Freeman
(2005).
How To Feed Friends and Influence People: The Carnegie Deli-- A
Giant Sandwich, a Little Deli, a Huge Success. (Hoboken,
NJ: Wiley, 192 p.). Carnegie Deli (Restaurant); Cookery, Jewish.
(Chez Panisse), Thomas McNamee; foreword by
R.W. Apple, Jr. (2007).
Alice Waters & Chez Panisse: The Romantic, Impractical, Often
Eccentric, Ultimately Brilliant Making of a Food Revolution.
(New York, NY: Penguin Press, 380 p.). Waters, Alice; Chez
Panisse; Restaurateurs--United States--Biography; Women
cooks--United States--Biography. Biography of Alice Waters and the
San Francisco 1970s counterculture food revolution that invented
"American cuisine."
 Alice Waters - Chez
Panisse
(http://www.edutopia.org/images/graphics/alice-waters.jpg)
Alice Waters - Chez
Panisse
(http://www.edutopia.org/images/graphics/alice-waters.jpg)
(Chick-Fil-A), S. Truett Cathy (1989).
It's Easier to Succeed Than To Fail. (Nashville, TN:
Oliver-Nelson, 192 p.). Cathy, S. Truett; Chick-Fil-A
Corporation--History; Businesspeople--United States--Biography;
Fast food restaurants--United States--History. Introduced
chicken sandwich concept to quick-service industry.
(Chick-Fil-A), S. Truett Cathy (2002).
Eat Mor Chikin: Inspire More People. (Decatur, GA:
Looking Glass Books, 200 p.). Cathy, S. Truett; Chick-Fil-A
Corporation--History; Restaurateurs--United States--Biography;
Fast food restaurants--United States--History.
(Chocolate Chocolate), Frances Park and Ginger
Park. (2011).
Chocolate Chocolate: The True Story of Two Sisters, Tons of
Treats, and the Little Shop That Could. (New York,
NY: St. Martin's/Dunne, 288 p.). Sisters, Founders of Chocolate
Chocolate. Park, Frances, 1955-; Park, Ginger; Chocolate
Chocolate (Firm); Chocolate industry --United States --History;
Candy industry --United States --History; Chocolate candy
--United States --History. January 1984 - Sisters opened
Chocolate Chocolate in downtown Washington, DC; transformed no
name shop into nationally celebrated boutique.
(CKE Restaurants, Inc.), Carl N. Karcher with
B. Carolyn Knight Karcher (1991). Never Stop Dreaming: Fifty
Years of Making it Happen. (San Marcos, CA: Robert Erdmann
Publ. Karcher, Carl Nicholas; CKE Restaurants, Inc.
(Coach & Horses ), Norman Balon with Spencer
Bright (1991).
You're Barred, You Bastards! (London, UK: Sidgwick &
Jackson, 184 p.). Balon, Norman, 1927- ; Coach & Horses
(Bar)--History; Restaurateurs--England--London--Biography.
(Coffee Republic), Sahar and Bobby Hashemi
(2004).
Anyone Can Do It: Building Coffee Republic from Our Kitchen
Table: 57 Real-Life Laws on Entrepreneurship.
(Chichester, West Sussex, UK: Capstone, 198 p. [orig. pub.
2002]). Coffee Republic (Firm) History; Coffeehouses Great
Britain History; Coffeehouses Great Britain Management; New
business enterprises Great Britain.
(Copacabana), Kristin Baggelaar (2006).
The Copacabana. (Charleston, SC: Arcadia Pub., 128 p.).
Copacabana (Night club : New York, N.Y.)--Pictorial works;
Entertainers--United States--Portraits.
Manhattan's best-known night
club, most popular nightspot in America.
(Copacabana), Mickey Podell-Raber with Charles
Pignone (10/1/2007).
The Copa: Jules Podell and the Hottest Club North of Havana.
(New York, NY: Collins, 256 p.). Daughter of longtime Copacabana
owner Jules Podell. Copacabana (Night club : New York, NY);
Music-halls (Variety-theaters, cabarets, etc.)--New York
(State)--New York--History--20th century. History of Jules Podell's
legendary club Copacabana; Russian immigrant dropped out of
fourth grade to make money for his family, created number one
destination for rich, famous, dangerous of New York.
(D & E Restaurant), Erlinda Enriquez Panlilio
(2000).
Teacher to Tycoon: The Life and Times of Trinidad Diaz Enriquez.
(Pasig City, Philippines: Anvil Pub., 309 p.). Enriquez,
Trinidad Diaz, 1908- ; Hotelkeepers--Philippines--Biography;
Restaurateurs--Philippines--Biography.
(Dairy Queen), Caroline H. Otis (1990).
The Cone with the Curl on Top: Celebrating Fifty Years 1940-1990.
(Minneapolis, MN: International Dairy Queen, 160 p.).
International Dairy Queen, Inc.--History; Ice cream
industry--United States--History.
(Dairy Queen), Bob Miglani (2006).
Treat Your Customers: Thirty Lessons on Service and Sales that I
Learned at My Family’s Dairy Queen Store (New York,
N.Y. : Hyperion, 152 p.). International Dairy Queen, Inc.;
Customer relations; Customer services. Winning strategies for
sales, service using anecdotes, analogies from 21-years of experience working at family’s
Dairy Queen®
store; coping with
angry customers, minimizing stress, making customer service
providers feel great about doing their jobs.
(Daniel), Leslie Brenner (2002).
The Fourth Star: Dispatches from Inside Daniel Boulud's
Celebrated New York Restaurant. (New York, NY: Clarkson
Potter, 314 p.). Food Writer. Boulud, Daniel; Daniel
(Restaurant).
(Delmonico's), Robert V.P. Steele (1967).
Delmonico's. (Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin, 374 p.).
Delmonico's.
(Delmonico's), Judith Choate, James Canora
photographs by Stev Pool (2008).
Dining at Delmonico's: A Trip Through Time at New York's Oldest
Restaurant. (New York, NY: Stewart, Tabori & Chang, 224
p.). Award-winning author and coauthor of more than 20
cookbooks; Corporate Chef of Delmonico’s; New York–based
photographer. Delmonico’s Restaurant (New York, N.Y.) --History;
Cookery. Country’s first real restaurant (opened
in Manhattan’s Financial District in 1837); first American
restaurant to use tablecloths, to offer private dining rooms, to
furnish a separate wine list, to admit women diners, to
re-envision haute cuisine for American palate; tradition of
exquisite food served in luxurious setting.
(Denny's), Jim Adamson with Rosemary Bray
McNatt and Robert McNatt (2000).
The Denny's Story: How a Company in Crisis Resurrected Its Good
Name and Reputation (New York, NY: Wiley, 205 p.).
Denny's, Inc.
(Domino's Pizza), Tom Monaghan with Robert
Anderson (1986).
Pizza Tiger. (New York, NY: Random House, 346 p.).
Monaghan, Tom, 1937- ; Domino's Pizza (Firm);
Restaurateurs--United States--Biography.
 Thomas S. Monaghan -
Domino's Pizza
(http://blog.mlive.com/businessreview/annarbor_impact/2008/12/
large_webp1monaghan.jpg)
Thomas S. Monaghan -
Domino's Pizza
(http://blog.mlive.com/businessreview/annarbor_impact/2008/12/
large_webp1monaghan.jpg)
(Dunkin' Donuts), William Rosenberg with
Jessica Brilliant Keener (2001).
Time To Make the Donuts. (New York, NY: Lebhar-Friedman
Books, 255 p.). Founder, Dunkin' Donuts. Rosenberg, William,
1916- ; Dunkin' Donuts (Firm) Biography; Dunkin' Donuts (Firm)
History; Restaurateurs United States Biography.; Businesspeople
United States Biography; Entrepreneurship United States;
Franchises (Retail trade) United States History.
(Elaine's), A.E. Hotchner (2004).
Everyone Comes to Elaine's: Forty Years of Neighborhood
Regulars, Movie Stars, All-Stars, Literary Lions, Financial
Scions, Top Cops, Politicians, and Power Brokers at the
Legendary Hot Spot. (New York, NY: Harper Entertainment,
256 p.). A Regular at Elaine's. Kaufman, Elaine; Elaine's
Restaurant (New York, N.Y.).
(El Bulli), Colman Andrews (2010).
Ferran: The Inside Story of El Bulli and the Man Who Reinvented
Food. (New York, NY: Gotham Books, 320 p.). Cofounder
and a Former Editor in Chief of Saveur. Adrià, Ferran; elBulli
(Restaurant) --History; Restaurateurs --Spain --Biography;
Avant-garde (Aesthetics). Ferran Adrià - arguably
today's greatest
culinary revolutionary; reservation harder than 50-yardline
tickets to Super Bowl; rise from resort-hotel dishwasher to
culinary deity; evolution of El Bulli from German-owned beach
bar to establishment voted annually by international jury as "the world's best restaurant"; Franco-era childhood near
Barcelona, El Bulli's creative "disco-beach" days, modern-day
creative wonderland of restaurant kitchen; original techniques:
deconstruction, spherification, creation of culinary foams and
airs; profoundly reimagined basic characteristics of food's
forms, celebrated, intensified natural flavors of raw materials;
creativity, imagination - genius that transcends
chef's métier, can inspire, enlighten; ways in which Adrià
has changed world, altered understanding, appreciation
of food and cooking.
 Ferran Adria - El Bulli (http://si.wsj.net/public/resources/images/OB-FJ539_ferran_G_20100127123922.jpg)
Ferran Adria - El Bulli (http://si.wsj.net/public/resources/images/OB-FJ539_ferran_G_20100127123922.jpg)
(Falls), David Blum (1992).
Flash in the Pan: The Life and Death of an American Restaurant.
(New York, NY: Simon and Schuster, 302 p.). Falls (Restaurant).
(Fior d'Italia), Francine Brevetti; Foreword
by John T. Lescroart (2005).
The Fabulous Fior - Over 100 Years in an Italian Kitchen.
(Nevada City, CA: San Francisco Bay Books, 170 p.).
Granddaughter of Waiter (Alberto Puccetti) at the Fior d'Italia
a Century Ago. Fior d'Italia; Italian cookery; San
Francisco--restaurants.
(Four Seasons), John Mariani with Alex Von
Bidder (1994).
The Four Seasons: A History of America's Premier Restaurant
(New York, NY: Crown, 205 p.). Four Seasons
(Restaurant)--history.
(Friendly's), S. Prestley Blake, Alan Farnham
(2011).
A Friendly Life. (St. Johnsbury, VT: Raphel
Marketing, 132 p.). Co-Founder; Former Senior Editor (Forbes).
Blake, S. Priestly; Friendly Ice Cream Corp. -- history.
(Fuddrucker's), Phil Romano with Steve
McLinden (2005).
Food for Thought: How the Creator of Fuddrucker's, Romano's
Macaroni Grill, and Eatzi's Built a $10 Billion Empire One
Concept at a Time. (Chicago, IL: Dearborn Financial
Pub., 224 p.). Restaurateur. Romano, Phil;
Restaurateurs--Biography.
 Phil Romano
- Fuddrucker's
(http://www.heroesforhumanity.com/myhero/img/Phil%2BRomano.jpg)
Phil Romano
- Fuddrucker's
(http://www.heroesforhumanity.com/myhero/img/Phil%2BRomano.jpg)
(Galatoire’s Restaurant), Marda Burton &
Kenneth Holditch (2004).
Galatoire’s: Biography of a Bistro. (Athens, GA: Hill
Street Press, 229 p.). Freelance Travel Journalist; Professor
Emeritus (University of New Orleans). Galatoire’s Restaurant.
(Golden Ball Tavern), Howard Gambrill, Jr.,
and Charles Hambrick-Stowe; introd. by Marley Brown (1977).
The Tavern and the Tory: The Story of the Golden Ball Tavern
(Weston, MA: Golden Ball Tavern Trust, 103 p.). Jones, Isaac,
1728-1813; Weston, Mass. Golden Ball Tavern;
Merchants--Massachusetts--Weston--Biography; Weston
(Mass.)--Biography.
(Great Race Pizza Shoppe), Robert P. Welsh
(1993).
3 Pies Hot!: A Race to Nowhere (Columbus, OH: Glass
Onion Publications, 272 p.). Great Race Pizza Shoppe, Inc.;
Restaurant management--Ohio; Pizza--Ohio.
(Green & Black’s), Craig Sams and Josephine
Fairley (2008).
Sweet Dreams: The Story of Green & Black’s. (London, UK:
Random House Business Books, 260 p.). Founders (husband, wife).
1991 - Craig Sams, Jo
Fairley launched organic chocolate bar; created name in 10
minutes ("Green" for organic button, "Black" for darkness
created by high cocoa content); became $100 million brand; 2003
- new investors, 5% stake acquired by Cadbury; 2005 - full
control acquired by Cadbury.
(Green Papaya), Lien Yeomans (2001).
Green Papaya: New Fruit from Old Seeds: How I Seduced Australia
with My Food. (Milsons Point, NSW: Random House
Australia, 222 p.). Yeomans, Lien; Green Papaya (Restaurant);
Restaurateurs--Australia--Biography; Women
cooks--Australia--Biography; Cookery, Vietnamese.
(Hamburger Hamlets Inc.), Marilyn Lewis
(2000).
"Marilyn, Are You Sure You Can Cook?" He Asked: A Memoir.
(Berkeley, CA: Ten Speed Press, 224 p.). Lewis, Marilyn, 1929- ;
Restaurateurs--United States--Biography; Cookery, American.
(Hardee's), Wilber Hardee (2000).
Life and Times of Wilber Hardee: Founder of Hardee's.
(Omaha, NE: iUniverse, 148 p.). Hardee, Wilber; Hardee's; fast
food restaurants--United States.
(Harry’s Bar), Arrigo Cipriani (1996).
Harry’s Bar: The Life and Times of the Legendary Venice Landmark.
(New York, NY: Arcade Pub., 188 p.). Harry’s Bar (Venice,
Italy)--History; Cookery, Italian; Celebrities--Social life and
customs. Founded 1931,
located just off the Palazzo San Marco.
(Fred Harvey), Lesley Poling-Kempes (1989).
The Harvey Girls: Women Who Opened the West. (New York,
NY: Paragon House, 252 p.). Fred Harvey (Firm)--History;
Waitresses--Southwest, New--History; Women--Southwest,
New--History; Tourism--Southwest, New--History; Southwest,
New--History--1848-; Southwest, New--Social conditions.

Fred
Harvey
(http://www.kshs.org/publicat/kaleidoscope/graphics/2002april_harvey.jpg)
(Fred Harvey), Kathleen L. Howard and Diana F.
Pardue; in cooperation with the Heard Museum; foreword by Martin
Sullivan (1996).
Inventing the Southwest: The Fred Harvey Company and Native
American Art. (Flagstaff, AZ: Northland Pub., 150 p.).
Fred Harvey (Firm)--History; Atchison, Topeka, and Santa Fe
Railway Company--History; Indian art--Southwest, New--History;
Pueblo art--History; Tourism--Southwest, New--History.
(Fred Harvey), Edited by Marta Weigle and
Barbara A. Babcock (1996).
The Great Southwest of the Fred Harvey Company and the Santa Fe
Railway. (Phoenix, AZ: Heard Museum, 254 p.). Fred
Harvey (Firm) --History; Atchison, Topeka, and Santa Fe Railway
Company --History; Pueblo art --History; Pueblo Indians
--Industries; Indian art --Southwest, New --History; Tourism
--Southwest, New --History; Indian Art --Collectors and
collecting --Southwest, New; Southwest, New --History --1848-.
Produced in connection with exhibit ’Inventing the
Southwest: The Fred Harvey Company and Native American Art,’
curated by Diana Pardue and Kathleen Howard".
(Fred Harvey),
Stephen Fried (2010).
Appetite for America: How Visionary Businessman Fred Harvey
Built a Railroad Hospitality Empire that Civilized the Wild West. (New
York, NY, Bantam Books, 544 p.). Investigative Journalist and
Essayist. Harvey, Fred; Fred Harvey (Firm); Restaurateurs
--United States --Biography; Cookery, American. Founding father
of nation’s service industry; family business civilized West,
introduced America to Americans, from 1880s through World War
II; Fred Harvey worked his way up from dishwasher to household
name, from single lunch counter into family empire of eating
houses and hotels along Atchison, Topeka, and Santa Fe railroad
(historic lodges still in use at Grand Canyon); patronized by
princes, presidents, countless travelers looking for best cup of
coffee in country; staff of carefully screened single young
women (celebrated Harvey Girls) - country’s first female
workforce.
(Horn & Hardart), Lorraine B. Diehl and
Marianne Hardart (2002).
The Automat: The History, Recipes, and Allure of the Art Deco
Masterpieces. (New York, NY: Clarkson/Potter, p.).
Vending machines.
 Joseph
Horn
(http://www.theautomat.net/images/horn.jpg)
Joseph
Horn
(http://www.theautomat.net/images/horn.jpg)
 Frank Hardart
(http://www.theautomat.net/images/hardart.jpg)
Frank Hardart
(http://www.theautomat.net/images/hardart.jpg)
(In-N-Out Burger), Stacy Perman (2009).
In-N-Out Burger: A Behind-the-Counter Look at the Fast-Food
Chain That Breaks All the Rules. (New York, NY:
HarperCollins, 352 p.). Writer (BusinessWeek). In-N-Out Burger
(Firm) --History; Fast food restaurants --United States
--History. Begun in tiny shack in 1948;
family-owned chain has refused to franchise, be
sold; cultural institution with insanely loyal following;
unique, profitable business exceeds all
expectations; family's struggle to maintain sustainable pop
empire against industry it helped pioneer, internal tensions,
bitter lawsuit threatened to bring company to brink;
counterintuitive approach to doing business; evolution of
California fad that transformed into enduring cult of
popularity.
 Harry, Esther Snyder
- In-N-Out Burger
(http://www.nhra.com/UserFiles/image/2011/News/July/snyder.gif)
Harry, Esther Snyder
- In-N-Out Burger
(http://www.nhra.com/UserFiles/image/2011/News/July/snyder.gif)
(Iron Horse Restaurant), Marilyn Pearsol
Giorgetti (2005).
From the Horse's Mouth: A Memoir of San Francisco's Legendary
Iron Horse Restaurant, Its Charismatic Owner, and the Giorgetti
Family. (Philadelphia, PA: Xlibris Corp., 128 p.). Iron
Horse Restaurant; San Francisco restaurants.
(Jockey), Lorenzo Diaz (1996).
Jockey, Historia de un Restaurante. (Barcelona, Spain:
Tusquets Editores, 260 p.). Jockey (Restaurant : Madrid,
Spain)--History.
(Carl Karcher), B. Carolyn
Knight (1981).
Making It Happen: The Story of Carl Karcher Enterprises.
(Anaheim, CA: C. Karcher Enterprises, 143 p.). Karcher, Carl
Nicholas; Carl Karcher Enterprises; Restaurateurs--United
States--Biography.
(KFC), Edward G. Klemm, Jr. (1980).
Claudia, The Story of Colonel Harland Sanders' Wife.
(Los Angeles, CA: Crescent Publications, 95 p.). Sanders,
Harland, 1890- ; Sanders, Claudia, 1902- ;
Restaurateurs--Kentucky--Biography; Wives--Kentucky--Biography.
 Colonel Harlan Sanders
(http://colonelsanders.com/images/bio_earlyyears.jpg)
Colonel Harlan Sanders
(http://colonelsanders.com/images/bio_earlyyears.jpg)
(KFC), John Ed Pearce (1982).
The Colonel: The Captivating Biography of the Dynamic Founder of
a Fast-Food Empire. (Garden City, NY: Doubleday, 225
p.). Sanders, Harland, 1890- ;
Restaurateurs--Kentucky--Biography.
(KFC), Robert Darden (2002).
Secret Recipe: Why KFC Is Still Cookin' After 50 Years.
(Dallas, TX: Tapestry Press, p.). Kentucky
Fried Chicken (Firm); Restaurant management.
(KFC), Bill Carey (2005).
Master of the Big Board: The Life, Times, and Businesses of Jack
C. Massey. (Nashville, TN: Cumberland House, 285 p.).
Massey, Jack C., 1904-1990; Businessmen --United States
--Biography; Capitalists and financiers --United States
--Biography. Only person
ever to take three companies to New York Stock Exchange; 1964 -
bought Harland Sanders's recipe, grew KFC into nationwide chain
of restaurants; s1968 - tarted Hospital Corporation of America,
chain of for-profit hospitals.
(KFC), Warren Liu (2008).
KFC in China: Recipe for Success. (Hoboken, NJ: Wiley,
191 p.). Vice President of Yum! Brands Greater China. Fried
Chicken (Firm); International business enterprises --China;
Franchises (Retail trade) --China --Marketing.
Major
contributing factors which catapulted KFC to top of Chinese
restaurant service industry in less than two decades;
industry leadership position in growth, profitability, market
share, brand recognition in world's fastest growing economy.
(Krispy Kreme), Kirk Kazanjian & Amy Joyner;
foreword by Dick Clark (2004).
Making Dough: The 12 Secret Ingredients of Krispy Kreme's Sweet
Success. (Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 222 p.). Television News
Anchor/Business Reporter; Business Reporter (News & Record in
North Carolina). Krispy Kreme Doughnuts; Baked products industry
United States Case studies.
(La Cote d'Or), William Echikson (1995).
Burgundy Stars: A Year in the Life of a Great French Restaurant.
(Boston, MA: Little, Brown, 311 p.). Loiseau, Bernard, 1951-; La
Côte d'Or (Restaurant); Cooks--France--Biography; Burgundy
(France)--Social life and customs.
 Bernard Loiseau
- La Côte d'Or
(http://newsimg.bbc.co.uk/media/images/38876000/jpg/_38876979_ap203bodyfood.jpg)
Bernard Loiseau
- La Côte d'Or
(http://newsimg.bbc.co.uk/media/images/38876000/jpg/_38876979_ap203bodyfood.jpg)
(La Cote d'Or), Rudolph Chelminski (2005).
The Perfectionist: Life and Death in Haute Cuisine. (New
York, NY: Gotham, 528 p.). Loiseau, Bernard, 1951-;
Cooks--France--Biography; Gastronomy.
(Le Cirque), Sirio Maccioni and Peter J.
Elliott (2004).
Sirio: The Story of My Life and Le Cirque. (Hoboken, NJ:
John Wiley & Sons, 432 p.,). Maccioni, Sirio; Le Cirque
(Restaurant); Restaurateurs--United States--Biography.
(The Legacy Companies), Neal Asbury (2010).
Conscientious Equity: An American Entrepreneur's Solutions to
the World's Greatest Problems. (New York, NY:
Palgrave Macmillan, 240p). Chief Executive of The Legacy
Companies; 2008 Recipient United States National Champion
Exporter of the Year Award. International trade; Free trade;
Competition, Unfair; Social justice. Restructuring of national
trade policy from intransigent political ideologies toward world
driven by fair international commerce addresses, solves economic
instability, destruction of environment, crushing poverty,
crippling corruption all over planet.
(Lil' Orbits Inc.), Ed Anderson (1998).
Climbing Jacob's Ladder to Wealth & Success: The Making of a
Millionaire. (Lakeville, MN: Galde Press, 190 p.).
Mini-Donut King. Anderson, Ed., 1931- ; Businessmen--United
States--Biography; Entrepreneurship--Biography; New business
enterprises--United States--Management.
(Locke-Ober), Ned and Pam Bradford (1978).
Boston's Locke-Ober Café: An Illustrated Social History with
Miscellaneous Recipes (New York, NY: Atheneum, 207 p.).
Locke-Ober Café (Boston, Mass.).
(Lomando Locatelli), Tony Allan (2006).
Making Good: The Inspiring Story of Serial Entrepreneur,
Maverick and Restaurateur. (London, UK: Capstone, 240
p.). Britain's Second Wealthiest Restaurateur. Lomando
Locatelli. Allan, Tony; Restaurants -- London;
Entrepreneurs--London--Biography. Meteoric rise from fishmonger to
elite of British entrepreneurs; what Tony Allan did, why he did
it the way he did; genuine rags-to-riches story.
(Luby’s Cafeterias Inc.), Carol Dawson and
Carol Johnston (2006).
House of Plenty The Rise, Fall, and Revival of Luby’s Cafeterias.
(Austin, TX: University of Texas Press, 288 p.). Writer; Only
Granddaughter of Lola Luby Johnston, Only Child of Luby's
Cofounder and Corporate Executive Charles R. Johnston and
Gertrude Johnston. Luby’s Cafeterias, Inc.--History;
Cafeterias--United States--History. Cafeteria empire that by the
1980s had revenues second only to McDonald's; financial failure
during 1990s with non-family leadership, struggle back to
solvency.
(Lucky Dogs Inc.), Jerry E. Strahan (1998).
Managing Ignatius: The Lunacy of Lucky Dogs and Life in the
Quarter. (Baton Rouge, LA: Louisiana State University
Press, 237 p.). Strahan, Jerry E., 1951- ; Talbot, Doug; Lucky
Dogs, Inc.--History; Hot dog stands--Louisiana--New Orleans; New
Orleans (La.)--Social life and customs.
(Lundy's), Robert Cornfield ; with recipes and
food notes by Kathy Gunst (1998).
Lundy's: Reminiscences and Recipes from Brooklyn's Legendary
Restaurant. (New York, NY: HarperCollins, 204 p.).
Lundy's (Restaurant)--History; Cookery (Seafood).
(Lutece), Irene Daria (1993).
Lutèce: A Day in the Life of America's Greatest Restaurant.
(New York, NY: Random House, 230 p.). Lutèce (Restaurant : New
York, N.Y.); Restaurants--New York (State)--New York.
(McDonald's), Max Boas and Steve Chain (1976).
Big Mac: The Unauthorized Story of McDonald's (New York,
NY: Dutton, 212 p.). McDonald's Corporation.
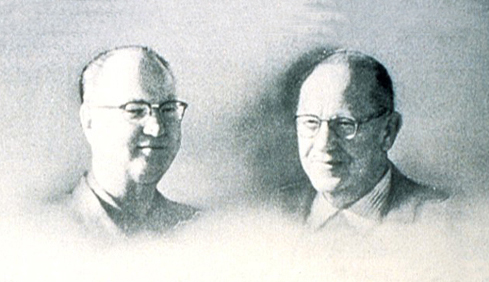 Richard and Maurice McDonald
(http://doney.net/aroundaz/celebrity/mcdonald_brothers.jpg)
Richard and Maurice McDonald
(http://doney.net/aroundaz/celebrity/mcdonald_brothers.jpg)
 Ray Kroc
-McDonald's
(http://www.mcdonalds.com/content/us/en/our_story/our_history/
the_ray_kroc_story/_jcr_content/
genericpagecontent/everything_0/image.img.jpg/1271053450190.jpg;
January 15, 1984
Obituary:
http://www.nytimes.com/learning/general/onthisday/bday/1005.html
Ray Kroc
-McDonald's
(http://www.mcdonalds.com/content/us/en/our_story/our_history/
the_ray_kroc_story/_jcr_content/
genericpagecontent/everything_0/image.img.jpg/1271053450190.jpg;
January 15, 1984
Obituary:
http://www.nytimes.com/learning/general/onthisday/bday/1005.html
(McDonald's), Edited by Marshall William
Fishwick (1983).
Ronald Revisited: The World of Ronald McDonald. (Bowling
Green, OH: Bowling Green University Popular Press, 157 p.).
McDonald's Corporation; Fast food restaurants -- United States.
(McDonald's), John F. Love (1986).
McDonald's: Behind the Arches (New York, NY: Bantam
Books, 470 p.). Kroc, Ray, 1902- ; McDonald's Corporation;
Restaurateurs--United States--Biography; Fast food
restaurants--United States.
(McDonald's), Ray Kroc; with Robert Anderson
(1987).
Grinding It Out: The Making of McDonald's (New York, NY:
St. Martin's Press, 218 p. [orig. pub. 1977]). Kroc, Ray, 1902-
; McDonald's Corporation; Restaurateurs--United
States--Biography.
(McDonald's), edited by James L. Watson
(1997).
Golden Arches East: McDonald's in East Asia (Stanford,
CA: Stanford University Press, 256 p.). McDonald's Corporation;
Fast food restaurants--East Asia.
(McDonald's), George Cohon; with David
Macfarlane (1997).
To Russia with Fries (Toronto, ON: M&S, 335 p.). Cohon,
George, 1937- ; McDonald's Corporation; McDonald's Corporation;
Restaurateurs--Canada--Biography; Fast food restaurants--Russia
(Federation); Fast food restaurants--Canada; Restaurateurs
(Alimentation)--Canada--Biographies; Restaurants-minute--Russie;
Restaurants-minute--Canada.
(McDonald's), John Vidal (1997).
McLibel: Burger Culture on Trial.
(New York, NY: New Press, 354 p.). Reporter (London Guardian).
Morris, David, 1954- --Trials, litigation, etc.; Steel,
Helen--Trials, litigation, etc.; McDonald's Corporation--Trials,
litigation, etc.; Trials (Libel)--England--London.
(McDonald's), Joe L. Kincheloe (2002).
The Sign of the Burger: McDonald's and the Culture of Power.
(Philadelphia, PA: Temple University Press, 232 p.). McDonald's
Corporation; Fast food restaurants--Social aspects; Restaurant
management; Consumer behavior; United States--Social
conditions--1945-.
(McDonald's), Paul Facella; with Adina Genn
(2008).
Everything I Know About Business I Learned at McDonald’s: The 7
Leadership Principles that Drive Break Out Success. (New
York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 256 p.). Former Regional Vice President
of the New York Region (34-Year Career at McDonald’s).
McDonald’s Corporation; Leadership; Success in business;
Management. McDonald's result-driven culture; core principles that have
successfully guided company for more than five decades; grew New York Region to $600 million
in revenues, four-fold increase in profit, 90% increase in store
count, one of strongest performing regions in country.
(Nepenthe), Romney Steele (2009).
My Nepenthe: Bohemian Tales of Food, Family, and Big Sur.
(Kansas City, MO, Andrews McMeel Pub., 352 p.). Granddaughter of
Bill and Lolly Fassett, creators of Nepenthe Restaurant. Steele,
Romney; Nepenthe Restaurant --History; Cookery, American
--California style. Famous California restaurant (1949) perched
on majestic cliffs of Big Sur, nestled among native oak trees
and historic log cabin, sweeping views of rugged Santa Lucia
Mountains, wild south coast of Monterey County; history of place
through food, Fassett family who started Nepenthe; about 250,000
people visit Nepenthe every year; family enterprise, Fassett
family and legacy; stories about family's more than sixty-year
history on the coast, arts and architecture, colorful people who
were genesis of legendary restaurant.
(Noah's Bagels), Noah Alper, Thomas
Fields-Meyer (2009).
Business Mensch: Timeless Wisdom for Today's Entrepreneur.
(Berkeley, CA, Book Clearing House, 176 p.). Founder of Noah's
Bagels. Alper, Noah; Entrepreneurship --California
--History. Started small bagel shop in Berkeley, CA (after early
nervous breakdown, failed business); run on Biblical injunction
to "lech lecha"-to embrace one's journey while contributing to
community through volunteerism and "tzedakah" - justice; ability
to innovate, adapt, and evolve; 2006 - acquired by Einstein Bros. for $100 million.
(Old French House Restaurant), Edward J.
Lepoma (1998). A
Passion for People: The Story of Mary Mahoney and Her Old French
House Restaurant. (Brandon, MS: Quail Ridge Press, 154
p.). Mahoney, Mary, 1924-1985; Old French House Restaurant;
Restaurateurs--Mississippi--Biloxi--Biography.
(Park Lane Restaurant), Ellen Taussig (1979).
Your Host, Peter Gust of the Park Lane Restaurant, His Story.
(Boston, MA: Herman Pub., 207 p.). Gust, Peter; Park Lane
Restaurant (Buffalo, N.Y.); Restaurateurs--New York
(State)--Buffalo--Biography.
(Pepe's North of the Border), Lyn Kidder
(1996).
Tacos on the Tundra: The Story of Barrow, Alaska's Long-Time
Resident, Fran Tate. (Anchorage, AK: Bonaparte Books,
266 p.). Tate, Fran, 1929- ; Pepe's North of the Border
(Restaurant); Restaurateurs--Alaska--Barrow--Biography; Barrow
(Alaska)--Description and travel.
(Rainforest Cafe), Steven Schussler, Marvin Karlins (2010).
It's a Jungle in There: Inspiring Lessons, Hard-Won Insights,
and Other Acts of Entrepreneurial Daring. (New York,
New York: Union Square Press, 256 p.). Founded the Rainforest
Cafe (record as top-grossing concept restaurant in US).
Schussler, Steven; Entrepreneurship; restaurants--United
States--history. Creativity to achieve dreams; principles for entrepreneurs on budget; lessons
can work in larger corporations:
self-branding, developing strategic partnerships, giving
recognition where due.
(Restaurant Associates), Lawrence Freundlich
(2000).
A Time Well Spent: A Biography of Jerome Brody. (New
York, NY: Welcome Rain, 236 p.). Brody, Jerome; Restaurant
Associates; restaurant management. How
Brody and handpicked team took Restaurant Associates from
failing cafeteria chain to highest levels of luxury dining;
invented theme restaurants; fired; created restaurant
empire of his own (Gallagher's Steakhouse, Grand Central Oyster
Bar).
(Russian Tea Room), Faith Stewart-Gordon
(1999).
The Russian Tea Room: A Love Story. (New York, NY:
Scribner, 250 p.). Wife-Husband Owners of The Russian Tea Room.
Stewart-Gordon, Faith--Biography; Russian Tea Room.
(Saga Corporation), William F. Scandling
(1994).
The Saga of Saga: The Life and Death of an American Dream.
(Mill Valley, CA: Vista Linda Press, 382 p.). Scandling, William
F.; Saga Corporation--History; Universities and colleges--Food
service--United States--History.
(Shenkel’s Restaurant), Edith Barr Dunn
(1986).
Lady from Longboat Key. (New York, NY: Carlton Press,
192 p.). Dunn, Edith Barr, 1920- ; Restaurateurs--United
States--Biography; Restaurant management--United States.
(Shoney's - founded 1947 by Alex Schoenbaum
and Ray Danner), Steve Watkins (1997).
The Black O: Racism and Redemption in an American Corporate
Empire. (Athens, GA: University of Georgia Press, 276
p.). Shoney's Inc.--Personnel management; Discrimination in
restaurants--United States--Case studies; Discrimination in
employment--United States--Case studies; Race
discrimination--United States--Case studies; African
Americans--Employment--Case studies.
(Sloppy Joe’s), Carol Shaughnessy (1995).
Sloppy Joe’s: The Tradition Continues. (Key West, FL:
Market Share Co., 58 p.). Hemingway, Ernest, 1899-1961 --Homes
and haunts--Florida--Key West; Sloppy Joe’s (Bar); Bars
(Drinking establishments)--Florida--Key West--History;
Novelists, American--20th century--Biography; Key West
(Fla.)--Intellectual life--20th century; Key West (Fla.)--Social
life and customs.
(Sonic),
Bob Blackburn (2009).
Sonic: The History
of America's Drive-in.
(Oklahoma City, OK, Cottonwood Publications, p.). Executive
Director of the Oklahoma Historical Society. Smith, Troy; Sonic
Drive-in; restaurants--United States--history.
(Starbucks), Howard Schultz and Dori Jones
Yang (1997).
Pour Your Heart into It: How Starbucks Built a Company One Cup
at a Time. (New York, NY: Hyperion, 351 p.). Starbucks
Coffee Company; Coffee industry--United States.
(Steak n Shake), Robert P. Cronin (2000).
Selling Steakburgers: The Growth of a Corporate Culture.
(Carmel, IN: Guild Press of Indiana, 112 p.). Cronin, Robert P.,
1924- ; Steak n Shake (Firm); Restaurateurs--United
States--Biography.
(Stork Club), Ralph Blumenthal (2000).
Stork Club: America's Most Famous Nightspot and the Lost World
of Cafe Society. (Boston, MA: Little, Brown, 296 p.).
Reporter (New York Times). Billingsley, Sherman; Stork Club (New
York, NY). How Stork Club came to be, why
it became an institution, why it died; 1934 - opened
as speakeasy front for Jazz Age
gangsters by Sherman Billingsley, former bootlegger from
Oklahoma; 1940s - peak; October 4,
1965 - closed, victim of battle over unionization,
charges of racism, changing culture.
 Sherman Billingsley
- Stork Club
(http://www.storkclub.org/graphics/billingsley.jpg)
Sherman Billingsley
- Stork Club
(http://www.storkclub.org/graphics/billingsley.jpg)
(Stuckey's), Elizabeth McCants Drinnon (1997).
Stuckey: The Biography of Williamson Sylvester Stuckey,
1909-1977. (Macon, GA: Mercer University Press, 131 p.).
Stuckey, Williamson Sylvester, 1910- ; Restaurateurs--United
States--Biography; Grocers--United States--Biography; Fast food
restaurants--United States--History; Convenience stores--United
States--History.
(Taco Bell), Debra Lee Baldwin (1999).
Taco Titan: The Glen Bell Story. (Arlington, TX: Summit
Publishing Group, p.). Bell, Glen William, 1923- ;
Taco Bell (Firm); Restaurateurs--United States--Biography; Fast
food restaurants--United States--History.
 Glen Bell
(http://www.tacobell.com.ph/images/glen_bell.gif)
Glen Bell
(http://www.tacobell.com.ph/images/glen_bell.gif)
(Tadich Grill), John Briscoe; foreword by
Michael Buich (2002).
Tadich Grill: The History of San Francisco's Oldest Restaurant,
with Recipes. (Berkeley, CA: Ten Speed Press, 186 p.).
Tadich Grill--History; Cookery, American.
(Tea & Sympathy), Anita Naughton (2002).
Tea & Sympathy: The Life of an English Tea Shop in New York.
(New York, NY: Putnam, p.). Waitress at Tea Shop. Tea & Sympathy
(Tea shop)--History; Cookery. 108 Greenwich St. (between 12th
and 13th Streets), opened on December 23, 1990.
(The Beautiful Helen), Tom Stone (2002).
The Summer of My Greek Taverna: A Memoir. (New York, NY:
Simon & Schuster, 250 p.). Stone, Tom--Travel--Greece--Patmos
Island; Restaurants--Greece--Patmos Island; Cookery, Greek;
Patmos Island (Greece)--Description and travel.
(Tim Hortons), Ron Buist (2003).
Tales from Under the Rim: The Marketing of Tim Hortons.
(Fredericton, NB: Goose Lane Editions, 218 p.). Former Marketing
Director at Tim Hortons for over 25 years. Tim Hortons;
Restaurant Management--Canada.
(Tour d’Argent), Claude Terrail (1974).
Ma Tour d’Argent. (Paris, FR: Stock, 526 p.). Owner.
Terrail, Claude; Tour d’argent (Restaurant); Cookery, French.

Claude Terrail - La
Tour d'Argent
(http://www.gayot.com/images/restaurants/claude_terrail.jpg)
--- (1982). La Tour d’Argent: Histoire et
Recettes du Plus Celebre Restaurant du Monde. (Paris, FR: JC
Lattes, 318 p.). Owner. Tour d’argent (Restaurant); Cookery,
French; Paris (France)--Buildings, structures, etc.
(Tour d’Argent), Claude Terrail (1997).
Le Roman de la Tour d’Argent. (Paris, FR: Le Cherche
midi e´diteur, 124 p.). Owner of Restaurant. Terrail, Claude;
Tour d’argent (Restaurant)--History.
(Trader Vic's), Trader Vic. Introd. by Herb
Caen (1973).
Frankly Speaking: Trader Vic's Own Story. (Garden City,
NY: Doubleday, 170 p.). Trader Vic; Restaurateurs--United
States--Biography; Cookery, International; Bergeron, Victor
Jules, Jr.
 Victor J. "Trader Vic" Bergeron
- Trader Vic's
(http://image2.findagrave.com/photos/2007/113/19073652_117747706316.jpg)
Victor J. "Trader Vic" Bergeron
- Trader Vic's
(http://image2.findagrave.com/photos/2007/113/19073652_117747706316.jpg)
(Tropicana), Rosa Lowinger and Ofelia Fox
(10/3/2005).
Tropicana Nights: The Life and Times of Havana's Legendary
Nightclub. (Orlando, FL: Harcourt, 448 p.). Cuban-Born
Journalist; Widow of the Tropicana’s Last Owner, Martín Fox.
Tropicana (Nightclub : Havana, Cuba)--History; Music-halls
(Variety-theaters, cabarets, etc.)--Cuba--Havana--History--20th
century.
(Charlie Trotter's), Edmund Lawler (2001).
Lessons in Service from Charlie Trotter. (Berkeley, CA:
Ten Speed Press, 233 p.). Charlie Trotter's (Restaurant);
Restaurant management.
(Union Square Hospitality
Group), Danny Meyer (2006).
Setting the Table: The Power of Hospitality in Restaurants,
Business, and Life. (New York, NY: HarperCollins, 336
p.). CEO of Union Square Hospitality Group. Meyer, Danny;
Restaurant management. "Enlightened Hospitality" ("how the delivery of that product
makes its recipient feel") - core of his business strategy.
(Victoria Station), Tom Blake (2006).
Prime Rib and Boxcars. Whatever Happened To Victoria Station?
(Dana Point, CA: Tooter's Publishing, 433 p.). Columnist for The
Orange County Register. Restaurant industry--history--1970s ;
Victoria Station. Rise, crash of Victoria Station; fastest growing restaurant
chain of 1970s; how company grew to over
100 restaurants in just over eight years; went from most-envied
restaurant chain to mismanaged disaster that ended in
bankruptcy.
(Washington Square Bar & Grill), Ron Fimrite;
foreword by Dan Jenkins (1988).
The Square: The Story of a Saloon. (Dallas, TX: Taylor
Pub. Co., 174 p.). (San Francisco, Calif.); San Francisco
(Calif.)--Social life and customs.
(Wendy's), R. David Thomas (1991).
Dave's Way: A New Approach to Old-Fashioned Success (New
York, NY: Putnam, 256 p.). Founder, Wendy's International.
Thomas, R. David, 1932- ; Wendy's International;
Restaurateurs--United States--Biography.
 Dave Thomas (http://www.meatindustryhalloffame.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/01/DaveThomas-150x150.jpg)
Dave Thomas (http://www.meatindustryhalloffame.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/01/DaveThomas-150x150.jpg)
(Wendy's), Dave Thomas with Ron Beyma (1994).
Dave Says-- Well Done!: The Common Guy's Guide to Everyday
Success. (Grand Rapids, MI: Zondervan Pub. House, 224
p.). Founder, Wendy's. Thomas, R. David, 1932- ; Success;
Success in business.
(Whataburger), Greg Wooldridge (2011).
The Whataburger Story, How One Man's Dream and One Woman's Heart
Inspired a Business to Become a Family. (Austin, TX
Texas Monthly Custom Pub., 160 p.). Dobson, Harmon; Whataburger,
L.P., fast food -- Texas -- history. 1950 - Harmon Dobson opened
up first Whataburger, small roadside hamburger stand, on Ayers
Street in Corpus Christi, TX (25 cent, all-American beef burgers
served on five-inch buns); 1967 - Grace Dobson (wife) took over;
passed on to three children; 2011 - family-owned and operated,
more than 700 locations in 10 states, annual sales of more than
$1 billion; more than 20,000 employees.
(White Castle), David Gerard Hogan (1997).
Selling 'Em by the Sack: White Castle and the Creation of
American Food. (New York, NY: New York University Press,
199 p.). Ingram, Billy, 1880-1966; Anderson, J. Walter, 1880- ;
White Castle (Restaurant)--History; Restaurateurs--United
States.
 Walt Anderson and Billy Ingram
- White Castle Systems, Inc.
(http://cdm16007.contentdm.oclc.org/utils/ajaxhelper/?CISOROOT=p267401coll32&CISOPTR=8878&action=2&DMSCALE=
08&DMWIDTH=500&DMHEIGHT=500)
Walt Anderson and Billy Ingram
- White Castle Systems, Inc.
(http://cdm16007.contentdm.oclc.org/utils/ajaxhelper/?CISOROOT=p267401coll32&CISOPTR=8878&action=2&DMSCALE=
08&DMWIDTH=500&DMHEIGHT=500)
(White Tower), Paul Hirshorn and Steven
Izenour (2007).
White Towers. (Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 189 p. [rev.
ed.]). Head of the Department of Architecture ( Drexel
University); principal in the Philadelphia firm Venturi, Scott
Brown and Associates, Inc. White Tower (Firm).
1926 - Thomas Saxe founded hamburger chain
in Milwaukee, WI; instantly recognizable buildings as
three-dimensional billboards; branding before age of branding;
evolution of restaurant chain, corporate culture, mass
marketing, rise of franchising in 20th century.
(Winston's), Herbert Whittaker, Arnold
Edinborough (1988).
Winston's: The Life and Times of a Great Restaurant.
(Don Mills, ON: Stoddart, 198 p.). Winston's (Restaurant) --
History; Restaurants -- Ontario -- Toronto -- History; Toronto
(Ont.) -- Social life and customs.
(Worcester Lunch Car Company), Richard J.S.
Gutman (2004).
The Worcester Lunch Car Company. (Portsmouth, NH:
Arcadia, 128 p.). Worcester Lunch Car
Company--History--Pictorial works; Diners
(Restaurants)--Massachusetts--Worcester--History--Pictorial
works; Wagons--Massachusetts--Worcester--History--Pictorial
works; Worcester (Mass.)--Buildings, structures, etc.--Pictorial
works; Worcester (Mass.)--History--Pictorial works; Worcester
(Mass.)--Social life and customs--Pictorial works.
1906 to 1961 - company built 651
diners (10 - 70 seats); oak, mahogany woodwork, intricate
ceramic tile patterns, backbar of stainless steel; distinctive
porcelain enamel exteriors.
(Yo! Sushi), Simon Woodroffe (2000).
The Book of Yo! (London, UK: Capstone, 60 p.). Founder,
Yo! Sushi, sushi bar in London. Woodrodde, Simonl Yo! sushi --
sushii restaurant; Entrepreneurs--London. Author's story and
wisdom for those starting a business and for general life.
(Yum! Brands), David Novak with John Boswell
(2007).
The Education of an Accidental CEO: My Journey from the Trailer
Park to the Corner Office. (New York, NY: Crown
Business, 32o p.). chairman and CEO of Yum! Brands, Inc. (KFC,
Pizza Hut, Taco Bell, Long John Silver’s, A&W All American
Food); Literary Agent, Book Packager, Author. Novak, David; Yum!
Brands (Firm); Restaurateurs--United States--Biography; Success
in business. Building
culture around reward, recognition, recognizing achievements of
others: getting ahead, getting noticed; motivating people,
turning businesses around; building winning teams, running
global company of nearly one million people; staying true to
yourself.
Bill Barich (2009).
Pint of Plain: Being an Account of the Decline of the
Traditional Irish Pub. (New York, NY: Walker, 256 p.).
Bars (Drinking establishments) --Ireland --History; Bars
(Drinking establishments) --Social aspects --Ireland.
State of
Irish pub today (missing
archetypal ideal portrayed in Ireland's literature); Irish culture at time of great change;
shift in country's values, identity.
Brian Cowan (2005).
The Social Life of Coffee: The Emergence of the British
Coffeehouse. (New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 384
p.). Canada Research Chair in Early Modern British History
(McGill University). Coffeehouses--History; Coffee--History.
Definitive account of the origins of
coffee drinking and coffeehouse society.
Phoebe Damrosch (2007).
Service Included: Four-Star Secrets of an Eavesdropping Waiter.
(New York, NY: Morrow, 240 p.). First female captain at Per Se
(New York City four-star restaurant). Damrosch, Phoebe, 1978- ;
Per Se (Restaurant); Waitresses--United States--Biography; Food
Service--New York (State)--New York--Anecdotes.
Obsession with food, affair with
a sommelier, observations of highly competitive, frenetic world
of fine dining; tips:1) do not ask waiter what else he or she
does; 2) do not steal waiter's pen; 3) do not say you're
allergic when you don't like something; 4) do not send something
back after eating most of it; 5) do not make faces or gagging
noises when hearing specials.
Robert L. Emerson (1979).
Fast Food: The Endless Shakeout. (New York, NY:
Lebhar-Friedman Books, 331 p.). Restaurants; Convenience foods.
Jim Heimann (1996).
Car Hops and Curb Service: A History of American Drive-In
Restaurants, 1920-1960. (San Francisco, CA: Chronicle
Books, 127 p.). Drive-in restaurants--United States--History.
--- (1998).
May I Take Your Order?: American Menu Design, 1920-1960.
(San Francisco, CA: Chronicle Books, 131 p.). Menu
design--United States--History--20th century.
Tom Higgins (1995).
Spotted Dick, s'Il Vous Plait : An English Restaurant in France.
(New York, NY: Soho Press, 248 p.). Restaurants--France--Lyon.
Ben Ryder Howe (2011).
My Korean Deli: Risking It All for a Convenience Store.
(New York, NY: Holt, 320 p.) .Former Senior Editor (The Paris
Review). Howe, Ben Ryder; Convenience stores --New York (State)
--New York; Delicatessens --New York (State) --New York; Korean
American business enterprises --New York (State) --New York;
Businesspeople --New York (State) --New York.
Author's wife, daughter of Korean immigrants,
bought store in Brooklyn for her parents; business struggled,
author commuted to Paris Review offices by day, sliced cold cuts,
sold lottery tickets at night; store's tumultuous life; transformative experience to salvage original gift,
and family, while sorting out
issues of values, work, identity.
Philip Langdon (1986).
Orange Roofs, Golden Arches: The Architecture of American Chain
Restaurants. (New York, NY: Knopf, 223 p.). Chain
restaurants--United States--Buildings.
Stan Luxenburg (1985).
Roadside Empires: How The Chains Franchised America.
(New York, NY: Viking, 313 p.). Fast-Food, Franchises (Retail
Trade).
John Mariani (1991).
America Eats Out: An Illustrated History of Restaurants,
Taverns, Coffee Shops, Speakeasies, and Other Establishments
That Have Fed Us for 350 Years (New York, NY: Morrow,
285 p.). Restaurants--United States--History; Taverns
(Inns)--United States--History.
Alice Foote MacDougall (1980).
The Autobiography of a Business Woman. (New York, NY:
Arno Press, 205 p. [orig. pub. 1928]). Ran chain of coffee
houses in New York. MacDougall, Alice Foote; Coffee houses.
MacDougall, Alice Foote, 1867-1945; Restaurateurs--New York
(State)--New York--Biography; Coffeehouses--New York
(State)--New York. Ran chain of coffee houses in New York.
Jerry Newman (2006).
My Secret Life on the McJob: Lessons from Behind the Counter
Guaranteed to Supersize Any Management Style. (New York,
NY: McGraw-Hill, 240 p.). University Distinguished Teaching
Professor (State University of New York at Buffalo). Fast food
restaurants--United States; Fast food restaurants--Social
aspects; Restaurant management. College professor went undercover
as bottom-rung worker for the biggest names in fast food; each
restaurant's respective manager determined climate of work
environment.
Richard Pillsbury (1990).
From Boarding House to Bistro: the American Restaurant Then and
Now. (Boston, MA: Unwin Hyman, 247 p.).
Restaurants--United States--History; Fast food
restaurants--United States--History; Diet--United States.
Ruth Reichl (2005).
Garlic and Sapphires: The Secret Life of a Critic in Disguise.
(New York, NY: Penguin, 352 p.). Former Restaurant Critic (New
York Times). Reichl, Ruth--Biography; Cookery.
Eric Schlosser (2001).
Fast Food Nation: The Dark Side of the All-American Meal.
(Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin, 356 p.). Fast food
restaurants--United States; Food industry and trade--United
States; Convenience foods--United States.
Steven A. Shaw (2005).
Turning the Tables: Restaurants from the Inside Out.
(New York, NY: HarperCollins, 240 p.). Former Attorney Turned
Food and Restaurant Critic in 1997. Restaurants.
Rebecca L. Spang (2000).
The Invention of the Restaurant: Paris and Modern Gastronomic
Culture. (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 325
p.). Restaurants--France--Paris--History--18th century;
Restaurants--France--Paris--History--19th century; Food
habits--France--Paris--History--18th century; Food
habits--France--Paris--History--19th century; Paris
(France)--Social life and customs.
Alan Warde and Lydia Martens (2000).
Eating Out: Social Differentiation, Consumption, and Pleasure.
(New York, NY: Cambridge University Press, 246 p.). Food
habits--England; Restaurants--England--Social aspects; Consumer
behavior--England; England--Social life and customs.
Jan Whitaker (2002).
Tea at the Blue Lantern Inn: A Social History of the Tea Room
Craze in America. (New York, NY: St. Martin’s Press, 192
p.). Tearooms --United States --History.; United States --Social
life and customs. Cultural institution that survives, thrives;
sparked by rise of automobile, advent of Prohibition, rumblings
of suffragist movement, general American inventiveness, women
across America started tea room craze - everywhere, from small
towns to big cities, fringes of bohemian scene in Greenwich
Village to high-society salons of grand hotels; offering way for
women to express their creativity, entrepreneurial spirit.
_________________________________________________________
Business History Links
American Diner Museum
http://www.dinermuseum.org/
This Rhode Island museum is "focused on celebrating and
preserving the cultural and historical significance of the
American diner, a unique American institution." Read about the
history of diners, learn diner slang, and find links to other
diner sites. Subjects: Diners (Restaurants)... Since 1996, the
American Diner Museum (ADM) has been focused on celebrating and
preserving the cultural and historical significance of the
American diner, a unique American institution. The museum also
hopes to recognize and share the importance of diners nationally
and internationally.
Bohn-Bettoni Collection
http://www.library.unlv.edu/speccol/menus/index.html
UNLV Special Collections houses one of the largest menu
collections in the United States. Purchased from Mrs. Marion
Bohn Knutson, daughter of Henry J. Bohn, owner, publisher,
editor of The Hotel World magazine in Chicago (1879-1930); had
purchased Henri Bettoni’s Recueil de Menus to add to his own
personal collection (Henri Bettoni was late 19th-century London
restaurateur, manager of number of London restaurants, including
Tracadero, Kuhn’s, Kissel’s Tivoli, Globe, Savoy Hotel; had also
managed Haxell’s Hotel in Brighton); Collection comprised
approximately 1500 menus dating from 1874 to 1933. Bohn’s own
collection derived principally from American Midwest, Bettoni
collection predominantly British and French with examples from
German, other European cities.
National Restaurant Association
Http://Www.Restaurant.Org/
Representing, Educating and Promoting the
Restaurant/Hospitality Industry.
Restaurant-ing Through History
http://victualling.wordpress.com/
Restaurants in American history, going all the way back to the
1700s. On top of that I’ve collected menus, postcards, leaflets,
business cards, etc.; very revealing of our culture’s humanity
(and lack thereof).
Restaurant Performance Index
(RPI)
http://www.restaurant.org/research/economy/rpi/
National Restaurant Association's Restaurant Performance
Index is a monthly composite index that tracks the health of and
outlook for the U.S. restaurant industry (released on the last
business day of each month, based on responses to the
Association's Restaurant Industry Tracking Survey, a monthly
survey of restaurateurs nationwide on key indicators, including
same-store sales, traffic, labor and capital expenditures. The
Index consists of two components -- the Current Situation Index
and the Expectations Index).
What America
Spends on Food and Drink
http://www.bundle.com/article/foodanddrink2010-10578
Grocery-dining out breakdown in major cities. The average
household in Austin spends the most money on food per year.
Atlanta has the highest skew towards spending on dining out at
57%. The US average is 37%. People making $40,000 to $50,000
spent $5,560 on food in 2009. People making more than $125,000
spent $12,655 — more than double (buy more expensive food);
people who are spending the most money on food overall devote
more money to dining out; as income rises, people spend more
money on restaurants.
|

